GSTP1 expression predicts poor pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in ER-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 22320227
- PMCID: PMC7659189
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2012.02231.x
GSTP1 expression predicts poor pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in ER-negative breast cancer
Abstract
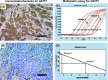
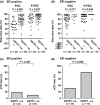
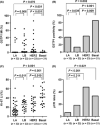
The purpose of the present study was to investigate the association of glutathione S-transferase P1 (GSTP1) expression with resistance to neoadjuvant paclitaxel followed by 5-fluorouracil/epirubicin/cyclophosphamide (P-FEC) in human breast cancers. The relationship of GSTP1 expression and GSTP1 promoter hypermethylation with intrinsic subtypes was also investigated. In this study, primary breast cancer patients (n = 123, stage II-III) treated with neoadjuvant P-FEC were analyzed. Tumor samples were obtained by vacuum-assisted core biopsy before P-FEC. GSTP1 expression was determined using immunohistochemistry, GSTP1 promoter methylation index (MI) using bisulfite methylation assay and intrinsic subtypes using DNA microarray. The pathological complete response (pCR) rate was significantly higher in GSTP1-negative tumors (80.0%) than GSTP1-positive tumors (30.6%) (P = 0.009) among estrogen receptor (ER)-negative tumors but not among ER-positive tumors (P = 0.267). Multivariate analysis showed that GSTP1 was the only predictive factor for pCR (P = 0.013) among ER-negative tumors. Luminal A, luminal B and HER2-enriched tumors showed a significantly lower GSTP1 positivity than basal-like tumors (P = 0.002, P < 0.001 and P = 0.009, respectively), while luminal A, luminal B and HER2-enriched tumors showed a higher GSTP1 MI than basal-like tumors (P = 0.076, P < 0.001 and P < 0.001, respectively). In conclusion, these results suggest the possibility that GSTP1 expression can predict pathological response to P-FEC in ER-negative tumors but not in ER-positive tumors. Additionally, GSTP1 promoter hypermethylation might be implicated more importantly in the pathogenesis of luminal A, luminal B and HER2-enriched tumors than basal-like tumors.
© 2012 Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures

References
-
- Kuerer HM, Newman LA, Smith TL et al Clinical course of breast cancer patients with complete pathologic primary tumor and axillary lymph node response to doxorubicin‐based neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17: 460–9. - PubMed
-
- Bear HD, Anderson S, Smith RE et al Sequential preoperative or postoperative docetaxel added to preoperative doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide for operable breast cancer: National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project Protocol B‐27. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 2019–27. - PubMed
-
- Liedtke C, Mazouni C, Hess KR et al Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long‐term survival in patients with triple‐negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 1275–81. - PubMed
-
- Sachelarie I, Grossbard ML, Chadha M, Feldman S, Ghesani M, Blum RH. Primary systemic therapy of breast cancer. Oncologist 2006; 11: 574–89. - PubMed
-
- Kaufmann M, von Minckwitz G, Bear HD et al Recommendations from an international expert panel on the use of neoadjuvant (primary) systemic treatment of operable breast cancer: new perspectives 2006. Ann Oncol 2007; 18: 1927–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

