Tumor-suppressive microRNA silenced by tumor-specific DNA hypermethylation in cancer cells
- PMID: 22320679
- PMCID: PMC7659391
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2012.02236.x
Tumor-suppressive microRNA silenced by tumor-specific DNA hypermethylation in cancer cells
Abstract
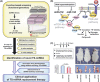
MicroRNA (miRNA) genes, located in intergenic or intragenic non-coding regions of the genome, are transcribed and processed to small non-protein-coding RNA of approximately 22 nucleotides negatively regulating gene expression. Some miRNA have already been reported for their genetic alterations, aberrant expression and oncogenic or tumor-suppressive functions. After 2008, there has been a striking increase in the number of publications reporting tumor-suppressive miRNA (TS-miRNA) silenced epigenetically in various types of cancers, suggesting important clinical applications for miRNA-based molecular diagnosis and therapy for cancers. Here, we introduce a correlation of the gene silencing of TS-miRNA through CpG island hypermethylation with the genomic distances between intergenic and intragenic miRNA genes or protein-coding host genes and CpG islands located around these genes. Furthermore, we also discuss the potential of miRNA replacement therapy for cancers using double-stranded RNA mimicking TS-miRNA.
© 2012 Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures


References
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 2004; 431: 350–5. - PubMed
-
- Mattick JS. RNA regulation: a new genetics? Nat Rev Genet 2004; 5: 316–23. - PubMed
-
- Brown JW, Marshall DF, Echeverria M. Intronic noncoding RNAs and splicing. Trends Plant Sci 2008; 13: 335–42. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004; 116: 281–97. - PubMed
-
- He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet 2004; 5: 522–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

