Inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling by CCI-779 (temsirolimus) induces growth inhibition and cell cycle arrest in Cashmere goat fetal fibroblasts (Capra hircus)
- PMID: 22320865
- PMCID: PMC3378953
- DOI: 10.1089/dna.2011.1559
Inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling by CCI-779 (temsirolimus) induces growth inhibition and cell cycle arrest in Cashmere goat fetal fibroblasts (Capra hircus)
Abstract
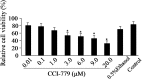
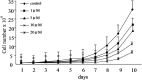
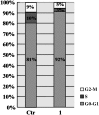
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a Ser/Thr kinase. It plays an evolutionarily conserved role in regulating cell growth, proliferation, survival, and metabolism via different cellular processes. The purpose of this study was to explore the inhibitory effects of CCI-779 (temsirolimus), a specific mTOR inhibitor, on mTOR signaling, and examine the mechanism of cell growth suppression by CCI-779 in Cashmere goat fetal fibroblasts (GFb cells). GFb cells were sensitive to CCI-779 and the survival rate of cells treated with >3.0 μM of CCI-779 was significantly reduced compared with the control (p<0.01). CCI-779 inhibited the phosphorylation of mTOR (at Ser2448) and S6 (at Ser240/244), and the expression of mTOR, p70S6K, and S6. Thus, CCI-779 was toxic to GFb cells, and it induced a dose-dependent decrease in cell proliferation and caused G1/S cell cycle arrest. Taken together, these data show that CCI-779 can inhibit mTOR signaling and proliferation in GFb cells in vitro. Therefore, mTOR is an important regulator for GFb cell growth and proliferation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A quantitative transcriptomic analysis of the physiological significance of mTOR signaling in goat fetal fibroblasts.BMC Genomics. 2016 Nov 7;17(1):879. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3151-y. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27821074 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization and functional analysis of Cashmere goat mammalian target of rapamycin.DNA Cell Biol. 2012 May;31(5):839-44. doi: 10.1089/dna.2011.1393. Epub 2011 Dec 16. DNA Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22176213 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic efficacy of inhibiting MYCN and mTOR signaling against neuroblastoma.BMC Cancer. 2021 Sep 26;21(1):1061. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08782-9. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34565342 Free PMC article.
-
Rapamycin and the inhibition of the secretory phenotype.Exp Gerontol. 2017 Aug;94:89-92. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2017.01.026. Epub 2017 Feb 4. Exp Gerontol. 2017. PMID: 28167236 Review.
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition as therapy for hematologic malignancies.Cancer. 2004 Feb 15;100(4):657-66. doi: 10.1002/cncr.20026. Cancer. 2004. PMID: 14770419 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphoproteomics Analysis Reveals a Pivotal Mechanism Related to Amino Acid Signals in Goat Fetal Fibroblast.Front Vet Sci. 2021 Aug 3;8:685548. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.685548. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 34414225 Free PMC article.
-
A quantitative transcriptomic analysis of the physiological significance of mTOR signaling in goat fetal fibroblasts.BMC Genomics. 2016 Nov 7;17(1):879. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3151-y. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27821074 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characterization and Expression Analysis of S6K1 in Cashmere Goats (Capra hircus).Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2013 Aug;26(8):1057-64. doi: 10.5713/ajas.2012.12710. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2013. PMID: 25049885 Free PMC article.
-
Celastrol induces cell cycle arrest by MicroRNA-21-mTOR-mediated inhibition p27 protein degradation in gastric cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2015 Oct 24;15:101. doi: 10.1186/s12935-015-0256-3. eCollection 2015. Cancer Cell Int. 2015. PMID: 26500453 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bajotto G. Sato Y. Kitaura Y. Shimomura Y. Effect of branched-chain amino acid supplementation during unloading on regulatory components of protein synthesis in atrophied soleus muscles. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011;111:1815–1828. - PubMed
-
- Berven L.A. Willard F.S. Crouch M.F. Role of the p70(S6K) pathway in regulating the actin cytoskeleton and cell migration. Exp Cell Res. 2004;296:183–195. - PubMed
-
- Burgos S.A. Dai M. Cant J.P. Nutrient availability and lactogenic hormones regulate mammary protein synthesis through the mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway. J Dairy Sci. 2010;93:153–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

