Inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling by CCI-779 (temsirolimus) induces growth inhibition and cell cycle arrest in Cashmere goat fetal fibroblasts (Capra hircus)
- PMID: 22320865
- PMCID: PMC3378953
- DOI: 10.1089/dna.2011.1559
Inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling by CCI-779 (temsirolimus) induces growth inhibition and cell cycle arrest in Cashmere goat fetal fibroblasts (Capra hircus)
Abstract
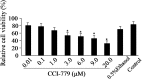
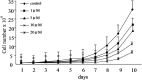
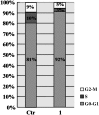
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a Ser/Thr kinase. It plays an evolutionarily conserved role in regulating cell growth, proliferation, survival, and metabolism via different cellular processes. The purpose of this study was to explore the inhibitory effects of CCI-779 (temsirolimus), a specific mTOR inhibitor, on mTOR signaling, and examine the mechanism of cell growth suppression by CCI-779 in Cashmere goat fetal fibroblasts (GFb cells). GFb cells were sensitive to CCI-779 and the survival rate of cells treated with >3.0 μM of CCI-779 was significantly reduced compared with the control (p<0.01). CCI-779 inhibited the phosphorylation of mTOR (at Ser2448) and S6 (at Ser240/244), and the expression of mTOR, p70S6K, and S6. Thus, CCI-779 was toxic to GFb cells, and it induced a dose-dependent decrease in cell proliferation and caused G1/S cell cycle arrest. Taken together, these data show that CCI-779 can inhibit mTOR signaling and proliferation in GFb cells in vitro. Therefore, mTOR is an important regulator for GFb cell growth and proliferation.
Figures

References
-
- Bajotto G. Sato Y. Kitaura Y. Shimomura Y. Effect of branched-chain amino acid supplementation during unloading on regulatory components of protein synthesis in atrophied soleus muscles. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011;111:1815–1828. - PubMed
-
- Berven L.A. Willard F.S. Crouch M.F. Role of the p70(S6K) pathway in regulating the actin cytoskeleton and cell migration. Exp Cell Res. 2004;296:183–195. - PubMed
-
- Burgos S.A. Dai M. Cant J.P. Nutrient availability and lactogenic hormones regulate mammary protein synthesis through the mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway. J Dairy Sci. 2010;93:153–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

