Recent progress toward understanding the physiological function of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- PMID: 22321024
- PMCID: PMC3403263
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2012.03567.x
Recent progress toward understanding the physiological function of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Abstract
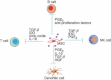
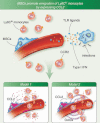
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are multipotent cells that are being clinically explored as regenerative therapeutics. Cultured MSCs secrete various modulatory factors, which contribute to the immunosuppressive effects of transplanted MSCs as a therapy. Although the in vitro phenotype of MSCs has been well characterized, identification of MSCs in vivo is made difficult by the lack of specific markers. Current advances in murine MSC research provide valuable tools for studying the localization and function of MSCs in vivo. Recent findings suggest that MSCs exert diverse functions depending on tissue context and physiological conditions. This review focuses on bone marrow MSCs and their roles in haematopoiesis and immune responses.
© 2012 The Author. Immunology © 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Friedenstein AJ, Petrakova KV, Kurolesova AI, Frolova GP. Heterotopic of bone marrow. Analysis of precursor cells for osteogenic and hematopoietic tissues. Transplantation. 1968;6:230–47. - PubMed
-
- Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8:315–17. - PubMed
-
- Simmons PJ, Torok-Storb B. Identification of stromal cell precursors in human bone marrow by a novel monoclonal antibody, STRO-1. Blood. 1991;78:55–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

