Epidermal growth factor receptor R521K polymorphism shows favorable outcomes in KRAS wild-type colorectal cancer patients treated with cetuximab-based chemotherapy
- PMID: 22321154
- PMCID: PMC7659261
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2012.02225.x
Epidermal growth factor receptor R521K polymorphism shows favorable outcomes in KRAS wild-type colorectal cancer patients treated with cetuximab-based chemotherapy
Abstract
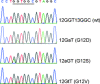
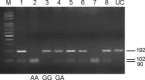
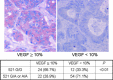
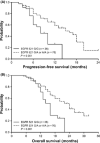
The R521K polymorphism of epidermal growth factor receptor has attenuated affinity in ligand binding and proto-oncogene induction, which may affect the efficacy of cetuximab. We analyzed the effect of this polymorphism on the outcome of 112 patients with KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal carcinoma treated with first-line cetuximab plus FOLFOX-4. The associations of this polymorphism with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression and clinicopathologic characteristics were also examined. The results showed that the frequencies of the G/G, G/A, and A/A genotypes were 32.1% (n = 36), 42.9% (n = 48), and 25.0% (n = 28), respectively. A marked decrease in VEGF expression levels (66.7% vs 28.9%, P < 0.01) was observed in patients with 521A allele variants (Arg/Lys or Lys/Lys), which were associated with a decreased tumor size (55.6% vs 31.6%, P = 0.02), good histological differentiation (63.9% vs 85.5%, P = 0.01), decreased lymphovascular invasion (69.4% vs 39.5%, P < 0.01), and a higher response rate to cetuximab plus FOLFOX treatment (55.6% vs 78.9%, P = 0.01). In addition, this polymorphism was associated with a longer progression-free period (P = 0.001) and overall survival (P = 0.001). By multivariate analysis, this polymorphism was also identified as an independent prognostic factor. These data suggest that the R521K polymorphism of epidermal growth factor receptor, by reducing its activation and a consequential downregulation of its target genes, including VEGF, could be a key determinant of an increased response to cetuximab-based chemotherapy and a longer survival for KRAS wild-type colorectal carcinoma patients.
© 2012 Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
Comment in
-
EGFR R521K predicts cetuximab response in KRAS wild-type patients.Pharmacogenomics. 2012 May;13(7):746. Pharmacogenomics. 2012. PMID: 22754965 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Activating KRAS mutations and overexpression of epidermal growth factor receptor as independent predictors in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with cetuximab.Ann Surg. 2010 Feb;251(2):254-60. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181bc9d96. Ann Surg. 2010. PMID: 20010090
-
Prospective analysis of KRAS wild-type patients with metastatic colorectal cancer using cetuximab plus FOLFIRI or FOLFOX4 treatment regimens.Genet Mol Res. 2011 Oct 3;10(4):3002-12. doi: 10.4238/2011.October.3.4. Genet Mol Res. 2011. PMID: 21968808
-
Cetuximab plus FOLFOX-4 in untreated patients with advanced colorectal cancer: a Gruppo Oncologico dell'Italia Meridionale Multicenter phase II study.Oncology. 2010;79(5-6):415-22. doi: 10.1159/000323279. Epub 2011 Apr 7. Oncology. 2010. PMID: 21474966 Clinical Trial.
-
Role of cetuximab in first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Apr 21;20(15):4208-19. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i15.4208. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24764659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-EGFR and anti-VEGF agents: important targeted therapies of colorectal liver metastases.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Apr 21;20(15):4263-75. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i15.4263. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24764664 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Investigation of Associations between TP53 rs1042522, BBC3 rs2032809, CCND1 rs9344, EGFR rs2227983 Polymorphisms and Breast Cancer Phenotype and Prognosis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Aug 5;11(8):1419. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11081419. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34441352 Free PMC article.
-
Association among polymorphisms in EGFR gene exons, lifestyle and risk of gastric cancer with gender differences in Chinese Han subjects.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59254. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059254. Epub 2013 Mar 29. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23555641 Free PMC article.
-
Two independent variants of epidermal growth factor receptor associated with risk of glioma in a Korean population.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 8;12(1):19014. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23217-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36347915 Free PMC article.
-
ErbB polymorphisms: insights and implications for response to targeted cancer therapeutics.Front Genet. 2015 Feb 4;6:17. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00017. eCollection 2015. Front Genet. 2015. PMID: 25699077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between polymorphisms in EGFR and tumor response during cetuximab and oxaliplatin-based combination therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: Analysis of data from two clinical trials.Oncol Lett. 2019 Nov;18(5):4555-4562. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10787. Epub 2019 Aug 29. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31611963 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ng M, Cunningham D. Cetuximab (Erbitux)‐an emerging targeted therapy for epidermal growth receptor‐expressing tumors. Int J Clin Pract 2004; 58: 970–6. - PubMed
-
- Pirker R, Pereira JR, Szczesna A et al Cetuximab plus chemotherapy in patients with advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer (FLEX): an open‐label randomised phase III trial. Lancet 2009; 373: 1497–8. - PubMed
-
- Chung KY, Shia J, Kemeny NE et al Cetuximab shows activity in colorectal cancer patients with tumors that do not express the epidermal growth factor receptor by immunohistochemistry. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 1803–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

