The structures of coiled-coil domains from type III secretion system translocators reveal homology to pore-forming toxins
- PMID: 22321794
- PMCID: PMC3304007
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.01.026
The structures of coiled-coil domains from type III secretion system translocators reveal homology to pore-forming toxins
Abstract
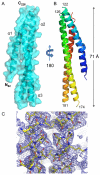
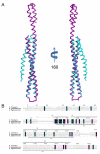
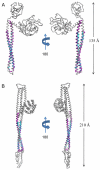
Many pathogenic Gram-negative bacteria utilize type III secretion systems (T3SSs) to alter the normal functions of target cells. Shigella flexneri uses its T3SS to invade human intestinal cells to cause bacillary dysentery (shigellosis) that is responsible for over one million deaths per year. The Shigella type III secretion apparatus is composed of a basal body spanning both bacterial membranes and an exposed oligomeric needle. Host altering effectors are secreted through this energized unidirectional conduit to promote bacterial invasion. The active needle tip complex of S. flexneri is composed of a tip protein, IpaD, and two pore-forming translocators, IpaB and IpaC. While the atomic structure of IpaD has been elucidated and studied, structural data on the hydrophobic translocators from the T3SS family remain elusive. We present here the crystal structures of a protease-stable fragment identified within the N-terminal regions of IpaB from S. flexneri and SipB from Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium determined at 2.1 Å and 2.8 Å limiting resolution, respectively. These newly identified domains are composed of extended-length (114 Å in IpaB and 71 Å in SipB) coiled-coil motifs that display a high degree of structural homology to one another despite the fact that they share only 21% sequence identity. Further structural comparisons also reveal substantial similarity to the coiled-coil regions of pore-forming proteins from other Gram-negative pathogens, notably, colicin Ia. This suggests that these mechanistically separate and functionally distinct membrane-targeting proteins may have diverged from a common ancestor during the course of pathogen-specific evolutionary events.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Diarrheal Diseases: Shigellosis. Vol. 2009. World Health Organization; 2009. http://www.who.int/vaccine_research/diseases/diarrhoeal/en/index6.html.
-
- Mueller C, Broz P, Cornelis G. The type III secretion system tip complex and translocon. Mol Microbiol. 2008;68:1085–95. - PubMed
-
- Cornelis GR. The type III secretion injectisome, a complex nanomachine for intracellular ‘toxin’ delivery. Biol Chem. 2010;391:745–51. - PubMed
-
- Blocker A, Jouihri N, Larquet E, Gounon P, Ebel F, Parsot C, Sansonetti P, Allaoui A. Structure and composition of the Shigella flexneri “needle complex”, a part of its type III secreton. Mol Microbiol. 2001;39:652–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

