Tumor-released survivin induces a type-2 t cell response and decreases cytotoxic T cell function, in vitro
- PMID: 22322461
- PMCID: PMC3601219
- DOI: 10.1007/s12307-012-0096-9
Tumor-released survivin induces a type-2 t cell response and decreases cytotoxic T cell function, in vitro
Abstract
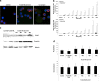
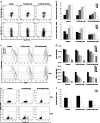
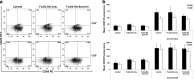
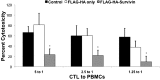
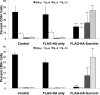
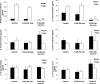
Clinical studies of T cell profiles from cancer patients have shown a skewing toward a type-2 T cell response with decreased cytotoxic T cell function. However, the primary cause of this shift remains unknown. Here we show that tumor-released Survivin, an inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) protein and tumor-specific antigen, is taken up by T cells and alters their response. The addition of Survivin to T cell cultures resulted in decreased T cell proliferation and reduced cytotoxic CD8(+) T cell function. Additionally, type 1 cell numbers and IFN-γ and IL-2 production were significantly reduced, while IL-4 release and type 2 T cell numbers increased. In contrast, the function and numbers of Th17 and T regulatory cells were not affected. These studies show that tumor-released Survivin modulates T cells resulting in a phenotype similar to that observed in cancer patients with a polarity shift from a type 1 to a type 2 response.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IFN-γ upregulates survivin and Ifi202 expression to induce survival and proliferation of tumor-specific T cells.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 22;5(11):e14076. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014076. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21124930 Free PMC article.
-
Smoking activates cytotoxic CD8+ T cells and causes survivin release in rheumatoid arthritis.J Autoimmun. 2017 Mar;78:101-110. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2016.12.009. Epub 2017 Jan 9. J Autoimmun. 2017. PMID: 28082047
-
The apoptosis inhibitor protein survivin induces tumor-specific CD8+ and CD4+ T cells in colorectal cancer patients.Cancer Res. 2003 Aug 1;63(15):4507-15. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12907624
-
Regulatory B and T cell responses in patients with autoimmune thyroid disease and healthy controls.Dan Med J. 2016 Feb;63(2):B5177. Dan Med J. 2016. PMID: 26836805 Review.
-
T-cell clones that react against autologous human tumors.Immunol Rev. 1990 Aug;116:33-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1990.tb00803.x. Immunol Rev. 1990. PMID: 2146210 Review.
Cited by
-
Exosomal survivin facilitates vesicle internalization.Oncotarget. 2018 Oct 9;9(79):34919-34934. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26182. eCollection 2018 Oct 9. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30405884 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting mTOR and survivin concurrently potentiates radiation therapy in renal cell carcinoma by suppressing DNA damage repair and amplifying mitotic catastrophe.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 6;43(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03079-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38840237 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Survivin Levels in Obstructive Sleep Apnoea.Lung. 2018 Aug;196(4):417-424. doi: 10.1007/s00408-018-0120-z. Epub 2018 May 8. Lung. 2018. PMID: 29740686
-
Anti-cancer effect of Annona Muricata Linn Leaves Crude Extract (AMCE) on breast cancer cell line.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Aug 24;16(1):311. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1290-y. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27558166 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating survivin levels in healthy and asthmatic pregnancy.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2014 Sep 23;12:93. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-12-93. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 25248821 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fiorentino DF, Zlotnik A, Vieira P, Mosmann TR, Howard M, Moore KW, O'Garra A. IL-10 acts on the antigen-presenting cell to inhibit cytokine production by Th1 cells. J Immunol. 1991;146:3444–3451. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

