Epiphany root canal sealer prepared with resinous solvent is irritating to rat subcutaneous tissues
- PMID: 22322512
- PMCID: PMC3476039
- DOI: 10.4317/medoral.17788
Epiphany root canal sealer prepared with resinous solvent is irritating to rat subcutaneous tissues
Abstract
Objective: This study assessed the biocompatibility of the Epiphany endodontic sealer prepared with resinous solvent of Epiphany system (Thinning resin) in rat subcutaneous tissues.
Study design: Polyethylene tubes were filled with the sealer and 4 groups were established: GI, Epiphany prepared with 1 drop of resinous solvent (RS); GII, Epiphany prepared with 1 drop of RS and photoactivated; GIII, Epiphany associated with self-etch primer and prepared with 1 drop of RS; GIV, Epiphany associated with self-etch primer, prepared with 1 drop of RS and photoactivated. The filled tubes were implanted into 4 different regions of the dorsum of 20 adult male rats.
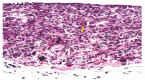
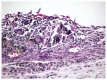
Results: After 7, 14 and 21 days, all groups presented a moderate to severe chronic inflammation, necrosis and foreign-body giant cells. At 42 days, although the intensity of chronic inflammatory reaction decreased, the other features still were observed.
Conclusion: The Epiphany sealer prepared with the RS was irritating to rat subcutaneous tissues.
Figures

References
-
- Hauman CH, Love RM. Biocompatibility of dental materials used in contemporary endodontic therapy: a review. Part 2. Root-canal-filling materials. Int Endod J. 2003;36:147–60. - PubMed
-
- Bernath M, Szabo J. Tissue reaction initiated by different sealers. Int Endod J. 2003;36:256–61. - PubMed
-
- Sousa CJ, Montes CR, Pascon EA, Loyola AM, Versiani MA. Comparison of the intraosseous biocompatibility of AH Plus, EndoREZ, and Epiphany root canal sealers. J Endod. 2006;32:656–62. - PubMed
-
- Merdad K, Pascon AE, Kulkarni G, Santerre P, Friedman S. Short-term cytotoxicity assessment of the epiphany resin-percha obturating system by indirect and direct contact millipore filter assays. J Endod. 2007;33:24–7. - PubMed
-
- Campos-Pinto MM, de Oliveira DA, Versiani MA, Silva-Sousa YT, de Sousa-Neto MD, da Cruz Perez DE. Assessment of the biocompatibility of Epiphany root canal sealer in rat subcutaneous tissues. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008;105:e77–81. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

