Resonance frequency analysis-reliability in third generation instruments: Osstell mentor®
- PMID: 22322519
- PMCID: PMC3482525
- DOI: 10.4317/medoral.17861
Resonance frequency analysis-reliability in third generation instruments: Osstell mentor®
Abstract
Few studies assess repeatability and reproducibility in registers of resonance frequency analysis (a value of dental implant stability).
Objective: Few studies assess repeatability and reproducibility in resonance frequency analyses (implant stability evaluation). This study is aimed at assessing reliability (repeatabilty and reproducibility) in the Osstell Mentor® system using the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) as the statistical method.
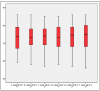
Study design: ISQ measurements of RFA were carried out by means of the Osstell Mentor® instrument in 58 implants in 19 patients. Six measurements were performed on each implant by means of two different Smart-Pegs (I and II). Three consecutive measurements were registered with each transducer.
Results: Average ISQ varied from 72.43 to 72.60 and 73.26 in the first, second and third measurements, respectively with the SamrtPeg I and from 72.98 to 73.26 and 73.74 in the first, second and third measurements, respectively with the SamrtPeg II . Exactly equal values were observed in 10.43 and 12.1% of the cases with Smart-Pegs I and II, respectively. The intraclass correlation coefficient was 0.96 and 0.96 for Smart Pegs I and II, respectively. Repeatability and reproducibility was 0.97 for both Smart-Pegs I and II.
Conclusions: The RFA system contributed by Osstell Mentor® renders almost perfect reproducibility and repeatability, as proven by statistical analysis carried out by means of ICC with 95% confidence level. This instrument contributes highly reliable RFA measurements in dental implants.
Figures
References
-
- Buser D, Mericske-Stern R, Bernard JP, Behneke A, Behneke N, Hirt HP et al. Long-term evaluation of nonsubmerged ITI implants. Part 1: 8-year life table analysis of a prospective multicenter study with 2359 implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1997;8:161–172. - PubMed
-
- Gapski R, Wang HL, Mascarenhas P, Lang NP. Critical review of immediate implant loading. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2003;14:515–27. - PubMed
-
- Rocci A, Martignoni M, Burgos PM, Gottlow J, Sennerby L. Histology of retrieved immediately and early loaded oxidizedimplants:Light microscopic observations after 5 to 9 monthsof loading in the posterior mandible. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2003;5(suppl 1):88–98. - PubMed
-
- Degidi M, Scarano A, Petrone G, Piattelli A. Histological analysis of clinically retrieved immediately loaded implants:Areport of 11 cases. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2003;5:89–93. - PubMed
-
- Weber HP, Morton D, Gallucci GO, Roccuzzo M, Cordaro L, Grutter L. Consensus statements and recommended clinical procedures regarding loading protocols. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:180–3. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources