Ca²⁺/cAMP-sensitive covariation of I(A) and I(H) voltage dependences tunes rebound firing in dopaminergic neurons
- PMID: 22323729
- PMCID: PMC6621702
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5297-11.2012
Ca²⁺/cAMP-sensitive covariation of I(A) and I(H) voltage dependences tunes rebound firing in dopaminergic neurons
Abstract
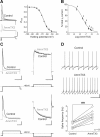
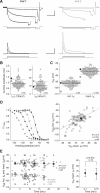
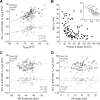
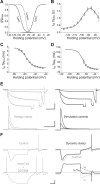
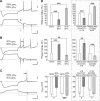
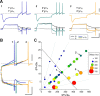
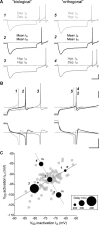
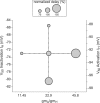
The level of expression of ion channels has been demonstrated to vary over a threefold to fourfold range from neuron to neuron, although the expression of distinct channels may be strongly correlated in the same neurons. We demonstrate that variability and covariation also apply to the biophysical properties of ion channels. We show that, in rat substantia nigra pars compacta dopaminergic neurons, the voltage dependences of the A-type (I(A)) and H-type (I(H)) currents exhibit a high degree of cell-to-cell variability, although they are strongly correlated in these cells. Our data also demonstrate that this cell-to-cell covariability of voltage dependences is sensitive to cytosolic cAMP and calcium levels. Finally, using dynamic clamp, we demonstrate that covarying I(A) and I(H) voltage dependences increases the dynamic range of rebound firing while covarying their amplitudes has a homeostatic effect on rebound firing. We propose that the covariation of voltage dependences of ion channels represents a flexible and energy-efficient way of tuning firing in neurons.
Figures



Comment in
-
Correlated voltage dependences of ion channels revealed.J Neurosci. 2012 May 23;32(21):7106-8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1133-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22623655 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- An WF, Bowlby MR, Betty M, Cao J, Ling HP, Mendoza G, Hinson JW, Mattsson KI, Strassle BW, Trimmer JS, Rhodes KJ. Modulation of A-type potassium channels by a family of calcium sensors. Nature. 2000;403:553–556. - PubMed
-
- Anderson D, Mehaffey WH, Iftinca M, Rehak R, Engbers JD, Hameed S, Zamponi GW, Turner RW. Regulation of neuronal activity by Cav3-Kv4 channel signaling complexes. Nat Neurosci. 2010;13:333–337. - PubMed
-
- Biel M, Wahl-Schott C, Michalakis S, Zong X. Hyperpolarization-activated cation channels: from genes to function. Physiol Rev. 2009;89:847–885. - PubMed
-
- Birnbaum SG, Varga AW, Yuan LL, Anderson AE, Sweatt JD, Schrader LA. Structure and function of Kv4-family transient potassium channels. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:803–833. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
