Fasting cycles retard growth of tumors and sensitize a range of cancer cell types to chemotherapy
- PMID: 22323820
- PMCID: PMC3608686
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003293
Fasting cycles retard growth of tumors and sensitize a range of cancer cell types to chemotherapy
Abstract
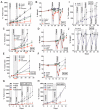
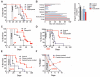
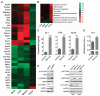
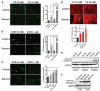
Short-term starvation (or fasting) protects normal cells, mice, and potentially humans from the harmful side effects of a variety of chemotherapy drugs. Here, we show that treatment with starvation conditions sensitized yeast cells (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) expressing the oncogene-like RAS2(val19) to oxidative stress and 15 of 17 mammalian cancer cell lines to chemotherapeutic agents. Cycles of starvation were as effective as chemotherapeutic agents in delaying progression of different tumors and increased the effectiveness of these drugs against melanoma, glioma, and breast cancer cells. In mouse models of neuroblastoma, fasting cycles plus chemotherapy drugs--but not either treatment alone--resulted in long-term cancer-free survival. In 4T1 breast cancer cells, short-term starvation resulted in increased phosphorylation of the stress-sensitizing Akt and S6 kinases, increased oxidative stress, caspase-3 cleavage, DNA damage, and apoptosis. These studies suggest that multiple cycles of fasting promote differential stress sensitization in a wide range of tumors and could potentially replace or augment the efficacy of certain chemotherapy drugs in the treatment of various cancers.
Figures

Comment in
-
Impersonalized medicine.Sci Transl Med. 2012 Mar 7;4(124):124ps6. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003738. Sci Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 22399263
References
-
- Longo VD, Finch CE. Evolutionary medicine: From dwarf model systems to healthy centenarians? Science. 2003;299:1342–1346. - PubMed
-
- Walford RL, Harris SB, Weindruch R. Dietary restriction and aging: Historical phases, mechanisms and current directions. J. Nutr. 1987;117:1650–1654. - PubMed
-
- Sinclair DA. Toward a unified theory of caloric restriction and longevity regulation. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2005;126:987–1002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

