Direct recruitment of polycomb repressive complex 1 to chromatin by core binding transcription factors
- PMID: 22325351
- PMCID: PMC3278717
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.11.032
Direct recruitment of polycomb repressive complex 1 to chromatin by core binding transcription factors
Abstract
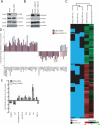
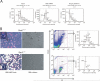
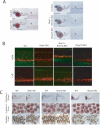
Polycomb repressive complexes (PRCs) play key roles in developmental epigenetic regulation. Yet the mechanisms that target PRCs to specific loci in mammalian cells remain incompletely understood. In this study we show that Bmi1, a core component of Polycomb Repressive Complex 1 (PRC1), binds directly to the Runx1/CBFβ transcription factor complex. Genome-wide studies in megakaryocytic cells demonstrate significant chromatin occupancy overlap between the PRC1 core component Ring1b and Runx1/CBFβ and functional regulation of a considerable fraction of commonly bound genes. Bmi1/Ring1b and Runx1/CBFβ deficiencies generate partial phenocopies of one another in vivo. We also show that Ring1b occupies key Runx1 binding sites in primary murine thymocytes and that this occurs via PRC2-independent mechanisms. Genetic depletion of Runx1 results in reduced Ring1b binding at these sites in vivo. These findings provide evidence for site-specific PRC1 chromatin recruitment by core binding transcription factors in mammalian cells.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Appleford PJ, Woollard A. RUNX genes find a niche in stem cell biology. J Cell Biochem. 2009;108:14–21. - PubMed
-
- Burns CE, DeBlasio T, Zhou Y, Zhang J, Zon L, Nimer SD. Isolation and characterization of runxa and runxb, zebrafish members of the runt family of transcriptional regulators. Exp Hematol. 2002;30:1381–1389. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

