Essential role of caveolin-3 in adiponectin signalsome formation and adiponectin cardioprotection
- PMID: 22328772
- PMCID: PMC3312581
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.242164
Essential role of caveolin-3 in adiponectin signalsome formation and adiponectin cardioprotection
Abstract
Objective: Adiponectin (APN) system malfunction is causatively related to increased cardiovascular morbidity/mortality in diabetic patients. The aim of the current study was to investigate molecular mechanisms responsible for APN transmembrane signaling and cardioprotection.
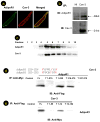
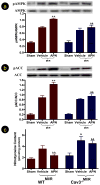
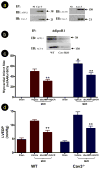
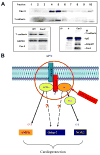
Methods and results: Compared with wild-type mice, caveolin-3 knockout (Cav-3KO) mice exhibited modestly increased myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury (increased infarct size, apoptosis, and poorer cardiac function recovery; P<0.05). Although the expression level of key APN signaling molecules was normal in Cav-3KO, the cardioprotective effects of APN observed in wild-type were either markedly reduced or completely lost in Cav-3KO. Molecular and cellular experiments revealed that APN receptor 1 (AdipoR1) colocalized with Cav-3, forming AdipoR1/Cav-3 complex via specific Cav-3 scaffolding domain binding motifs. AdipoR1/Cav-3 interaction was required for APN-initiated AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-dependent and AMPK-independent intracellular cardioprotective signalings. More importantly, APPL1 and adenylate cyclase, 2 immediately downstream molecules required for AMPK-dependent and AMPK-independent signaling, respectively, formed a protein complex with AdipoR1 in a Cav-3 dependent fashion. Finally, pharmacological activation of both AMPK plus protein kinase A significantly reduced myocardial infarct size and improved cardiac function in Cav-3KO animals.
Conclusions: Taken together, these results demonstrated for the first time that Cav-3 plays an essential role in APN transmembrane signaling and APN anti-ischemic/cardioprotective actions.
Figures


References
-
- Norhammar A, Lindback J, Ryden L, Wallentin L, Stenestrand U. Improved but still high short-and long-term mortality rates after myocardial infarction in patients with diabetes mellitus: a time-trend report from the Swedish Register of Information and Knowledge about Swedish Heart Intensive Care Admission. Heart. 2007;93:1577–1583. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Basu R, Pajvani UB, Rizza RA, Scherer PE. Selective Downregulation of the High Molecular Weight form (HMW) of Adiponectin in Hyperinsulinemia and in Type 2 Diabetes: Differential Regulation from Non-diabetic Subjects. Diabetes. 2007;56:2174–2177. - PubMed
-
- Tao L, Gao E, Jiao X, Yuan Y, Li S, Christopher TA, Lopez BL, Koch W, Chan L, Goldstein BJ, Ma XL. Adiponectin cardioprotection after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion involves the reduction of oxidative/nitrative stress. Circulation. 2007;115:1408–1416. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

