Assessing the feasibility of subepidermal moisture to predict erythema and stage 1 pressure ulcers in persons with spinal cord injury: a pilot study
- PMID: 22330190
- PMCID: PMC3240916
- DOI: 10.1179/204577211X13209212104141
Assessing the feasibility of subepidermal moisture to predict erythema and stage 1 pressure ulcers in persons with spinal cord injury: a pilot study
Abstract
Background: Persons with spinal cord injury (SCI) are at high risk for pressure ulcers (PrUs) throughout their lifetime due to decreased mobility, lack of sensation, and other physiological changes. The high prevalence and recurrence rates, and costs associated with PrUs in veterans with SCI indicate the need for a reliable and practical method of detecting early PrUs.
Objective: To assess the feasibility of obtaining biophysical measures of sub-epidermal moisture (SEM) using a handheld dermal phase meter to predict PrUs.
Design/methods: Prospective observational design. Thirty-four veterans at two VA SCI centers (Hines, Long Beach) received daily (n = 12) or weekly (n = 22) SEM and concurrent visual skin assessment (VSA) across nine anatomic locations for up to 6 weeks. Outcome measures: SEM, visual skin assessment (VSA), and stage I PrUs.
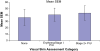
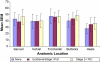
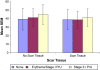
Findings/results: SEM was lowest for normal skin (39.3 dermal phase units (DPU), SD = 12.6) and higher for erythema/stage 1 PrUs (40.8 DPU, SD = 10.4) across all anatomic sites. Buttocks SEM were different between normal skin (40.5 DPU, SD = 10.3) and erythema/stage1 PrUs (43.8, SD = 9.5). SEM taken at heels were lower across all skin conditions (normal skin 28.2 DPU; erythema/stage 1 PrUs 34.7 DPU). SEM was taken when generalized edema present was lower than without generalized edema.
Conclusions: Preliminary results of using SEM to detect early PrU damage may translate from nursing home (NH) residents to persons with SCI. This study provides a foundation for a larger study to implement and assess SEM use as a method of prevention of PrUs.
Figures
References
-
- Mawson AR, Biundo JJ, Neville P, Linares HA, Winchester Y, Lopez A. Risk factors for early occurring pressure ulcers following spinal cord injury. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 1988;67(3):123–7 - PubMed
-
- Young JS, Burns PE. Pressure sores and the spinal cord injured. SCI Digest 1981;3:9–25
-
- Young JS, Burns PE. Pressure sores and the spinal cord injured, Part II. SCI Digest 1981;3:11–48
-
- Chen D, Apple DF, Hudson MF, Bode R. Medical complications during acute rehabilitation following spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1999;80(11):1397–401 - PubMed
-
- Fuhrer MJ, Garber SL, Rintala DH, Clearman R, Hart KA. Pressure ulcers in community-resident persons with spinal cord injury: prevalence and risk factors. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1993;74(11):1172–7 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical