The clinical value of the Tei index among Nigerians with hypertensive heart failure: correlation with other conventional indices
- PMID: 22331251
- PMCID: PMC3721940
- DOI: 10.5830/CVJA-2011-032
The clinical value of the Tei index among Nigerians with hypertensive heart failure: correlation with other conventional indices
Abstract
Background: Various conventional methods are used for functional evaluation and risk stratification in heart failure. A combined index of global myocardial performance called the Tei index has been described. The aim of this study was to evaluate the correlation of the Tei index with other conventional indices of systolic and diastolic function among Nigerians with hypertensive heart failure.
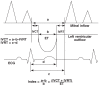
Methods: Fifty-five subjects with hypertensive heart failure and 30 controls were examined, a clinical history was taken, and echocardiography was performed on them. The subjects were categorised into four groups based on their ejection fraction (normal ejection fraction, mild, moderate and severe heart failure). The Tei index was calculated as the sum of the isovolumic relaxation and contraction time, divided by the ejection time. Statistical analysis was done using SPSS 16.0.
Results: The Tei index was significantly higher among subjects with hypertensive heart failure compared with the controls (0.91 ± 0.33 vs 0.28 ± 0.16, p < 0.005). The Tei index also increased with the severity of the heart failure and was inversely correlated with ejection fraction (r = -0.697, p < 0.001) and fractional shortening (r = -0.580, p = 0.001). It was directly correlated with mitral E/A ratio (r = 0.246, p = 0.030), left ventricular internal diastolic dimension (r = 0.414, p = 0.002), left ventricular internal systolic dimension (r = 0.596, p < 0.001) and deceleration time (r = 0.219, p = 0.032).
Conclusion: The Tei index correlated significantly with other conventional indices of systolic and diastolic function among Nigerians with hypertensive heart failure. It can be used as a risk-stratification index similar to other traditional indices of systolic and diastolic function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tei-index in patients with mild-to-moderate congestive heart failure.Eur Heart J. 2000 Nov;21(22):1888-95. doi: 10.1053/euhj.2000.2246. Eur Heart J. 2000. PMID: 11052862
-
Independent determinants of the Tei index in hypertensive patients with preserved left ventricular systolic function.Int Heart J. 2009 May;50(3):331-40. doi: 10.1536/ihj.50.331. Int Heart J. 2009. PMID: 19506337
-
Severe aortic valve stenosis with preserved and reduced systolic left ventricular function: diagnostic usefulness of the Tei index.J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2002 Sep;15(9):869-76. doi: 10.1067/mje.2002.120977. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2002. PMID: 12221402
-
Relationship between Tei index of myocardial performance and left ventricular geometry in Nigerians with systemic hypertension.Cardiovasc J Afr. 2011 May-Jun;22(3):124-7. doi: 10.5830/cvja-2010-050. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2011. PMID: 21713301 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical aspects of left ventricular diastolic function assessed by Doppler echocardiography following acute myocardial infarction.Dan Med Bull. 2001 Nov;48(4):199-210. Dan Med Bull. 2001. PMID: 11767125 Review.
Cited by
-
Improvement of the myocardial performance index in atrial fibrilation patients treated with amiodarone after cardioversion.J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2015 Mar;42(2):107-15. doi: 10.1007/s10840-014-9965-0. Epub 2015 Jan 16. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2015. PMID: 25591725
-
Clinical and Echocardiographic Predictors of Arrhythmias Detected With 24-Hour Holter Electrocardiography Among Hypertensive Heart Failure Patients in Nigeria.Clin Med Insights Cardiol. 2017 Dec 10;11:1179546817746632. doi: 10.1177/1179546817746632. eCollection 2017. Clin Med Insights Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 29270037 Free PMC article.
-
Right ventricular function in patients with heart failure in a cardiac clinic in Southwest Nigeria.Niger Med J. 2017 Jan-Feb;58(1):7-12. doi: 10.4103/0300-1652.218411. Niger Med J. 2017. PMID: 29238122 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic indices among hypertensive heart failure patients in Nigeria: the roles of 24-hour Holter electrocardiography and 6-minute walk test.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2017 Feb 27;13:71-79. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S124477. eCollection 2017. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2017. PMID: 28280349 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Assessment of Echocardiographic Patterns Among Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients on Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor and Healthy Controls.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2022 Feb 15;18:27-42. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S348744. eCollection 2022. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2022. PMID: 35210781 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Commerford P, Mayosi B. An appropriate research agenda for heart disease in Africa. Lancet. 2006;367:1884–1886. - PubMed
-
- Stewart S. Prognosis of patients with heart failure compared with common types of cancer. Heart Fail Monit. 2003;3(3):87–94. - PubMed
-
- Szucs TD, Sokolovic E. Economic significance of heart failure. Herz. 2000;25(5):538–546. - PubMed
-
- Schiller NB, Shah PM, Crawford M, DeMaria A, Devereux R, Feigenbaum H. et al. Recommendations for quantification of the left ventricle by two-dimensional echocardiography. J Am Soc Echo. 1989;2:358–367. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources