Epithelial organization and cyst lumen expansion require efficient Sec13-Sec31-driven secretion
- PMID: 22331354
- PMCID: PMC3367830
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.091355
Epithelial organization and cyst lumen expansion require efficient Sec13-Sec31-driven secretion
Abstract
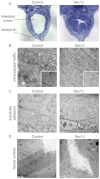
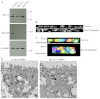
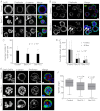
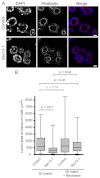
Epithelial morphogenesis is directed by interactions with the underlying extracellular matrix. Secretion of collagen and other matrix components requires efficient coat complex II (COPII) vesicle formation at the endoplasmic reticulum. Here, we show that suppression of the outer layer COPII component, Sec13, in zebrafish embryos results in a disorganized gut epithelium. In human intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2), Sec13 depletion causes defective epithelial polarity and organization on permeable supports. Defects are seen in the ability of cells to adhere to the substrate, form a monolayer and form intercellular junctions. When embedded in a three-dimensional matrix, Sec13-depleted Caco-2 cells form cysts but, unlike controls, are defective in lumen expansion. Incorporation of primary fibroblasts within the three-dimensional culture substantially restores normal morphogenesis. We conclude that efficient COPII-dependent secretion, notably assembly of Sec13-Sec31, is required to drive epithelial morphogenesis in both two- and three-dimensional cultures in vitro, as well as in vivo. Our results provide insight into the role of COPII in epithelial morphogenesis and have implications for the interpretation of epithelial polarity and organization assays in cell culture.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Efficient coupling of Sec23-Sec24 to Sec13-Sec31 drives COPII-dependent collagen secretion and is essential for normal craniofacial development.J Cell Sci. 2008 Sep 15;121(Pt 18):3025-34. doi: 10.1242/jcs.031070. Epub 2008 Aug 19. J Cell Sci. 2008. PMID: 18713835
-
Sec13 safeguards the integrity of the endoplasmic reticulum and organogenesis of the digestive system in zebrafish.Dev Biol. 2012 Jul 15;367(2):197-207. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.05.004. Epub 2012 May 15. Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22609279
-
The nuclear pore complex function of Sec13 protein is required for cell survival during retinal development.J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 25;289(17):11971-11985. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.547190. Epub 2014 Mar 13. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24627485 Free PMC article.
-
The highly conserved COPII coat complex sorts cargo from the endoplasmic reticulum and targets it to the golgi.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Feb 1;5(2):a013367. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a013367. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23378591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traffic jams in fish bones: ER-to-Golgi protein transport during zebrafish development.Cell Adh Migr. 2011 Mar-Apr;5(2):114-8. doi: 10.4161/cam.5.2.14377. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Cell Adh Migr. 2011. PMID: 21178403 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sec13 promotes oligodendrocyte differentiation and myelin repair through autocrine pleiotrophin signaling.J Clin Invest. 2022 Apr 1;132(7):e155096. doi: 10.1172/JCI155096. J Clin Invest. 2022. PMID: 35143418 Free PMC article.
-
Cargo selection in endoplasmic reticulum-to-Golgi transport and relevant diseases.J Clin Invest. 2023 Jan 3;133(1):e163838. doi: 10.1172/JCI163838. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 36594468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biophysical Control of Bile Duct Epithelial Morphogenesis in Natural and Synthetic Scaffolds.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019 Dec 13;7:417. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00417. eCollection 2019. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31921820 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo cell biology in zebrafish - providing insights into vertebrate development and disease.J Cell Sci. 2014 Feb 1;127(Pt 3):485-95. doi: 10.1242/jcs.140194. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 24481493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The biosynthetic-secretory pathway, supplemented by recycling routes, determines epithelial membrane polarity.Sci Adv. 2023 Jun 28;9(26):eade4620. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ade4620. Epub 2023 Jun 28. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37379377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrams E. W., Andrew D. J. (2005). CrebA regulates secretory activity in the Drosophila salivary gland and epidermis. Development 132, 2743-2758 - PubMed
-
- Antonny B., Madden D., Hamamoto S., Orci L., Schekman R. (2001). Dynamics of the COPII coat with GTP and stable analogues. Nat. Cell Biol. 3, 531-537 - PubMed
-
- Aridor M., Bannykh S. I., Rowe T., Balch W. E. (1999). Cargo can modulate COPII vesicle formation from the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 4389-4399 - PubMed
-
- Barlowe C., Orci L., Yeung T., Hosobuchi M., Hamamoto S., Salama N., Rexach M. F., Ravazzola M., Amherdt M., Schekman R. (1994). COPII: a membrane coat formed by Sec proteins that drive vesicle budding from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell 77, 895-907 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- E019633/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- G117/554/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G117/553/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0801848/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/E019633/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

