Expression and function of transforming growth factor β in melioidosis
- PMID: 22331429
- PMCID: PMC3347439
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.05534-11
Expression and function of transforming growth factor β in melioidosis
Abstract
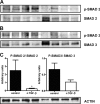
Melioidosis, caused by the Gram-negative bacterium Burkholderia pseudomallei, is an important cause of community-acquired sepsis in Southeast Asia and northern Australia. An important controller of the immune system is the pleiotropic cytokine transforming growth factor β (TGF-β), of which Smad2 and Smad3 are the major signal transducers. In this study, we aimed to characterize TGF-β expression and function in experimental melioidosis. TGF-β expression was determined in 33 patients with culture-proven infection with B. pseudomallei and 30 healthy controls. We found that plasma TGF-β concentrations were strongly elevated during melioidosis. In line with this finding, TGF-β expression in C57BL/6 mice intranasally inoculated with B. pseudomallei was enhanced as well. To assess the role of TGF-β, we inhibited TGF-β using a selective murine TGF-β antibody. Treatment of mice with anti-TGF-β antibody resulted in decreased lung Smad2 phosphorylation. TGF-β blockade appeared to be protective: mice treated with anti-TGF-β antibody and subsequently infected with B. pseudomallei showed diminished bacterial loads. Moreover, less distant organ injury was observed in anti-TGF-β treated mice as shown by reduced blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and aspartate transaminase (AST) values. However, anti-TGF-β treatment did not have an effect on survival. In conclusion, TGF-β is upregulated during B. pseudomallei infection and plays a limited but proinflammatory role during experimental melioidosis.
Figures



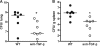

Similar articles
-
Gene Expression Profile of Human Cytokines in Response to Burkholderia pseudomallei Infection.mSphere. 2017 Apr 19;2(2):e00121-17. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00121-17. eCollection 2017 Mar-Apr. mSphere. 2017. PMID: 28435890 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous α2-antiplasmin is protective during severe gram-negative sepsis (melioidosis).Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013 Oct 15;188(8):967-75. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201307-1344OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013. PMID: 23992406
-
Toll-like receptor 2 impairs host defense in gram-negative sepsis caused by Burkholderia pseudomallei (Melioidosis).PLoS Med. 2007 Jul 31;4(7):e248. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040248. PLoS Med. 2007. PMID: 17676990 Free PMC article.
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor type I contributes to protective immunity during experimental Gram-negative sepsis (melioidosis).J Thromb Haemost. 2011 Oct;9(10):2020-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2011.04473.x. J Thromb Haemost. 2011. PMID: 21848642
-
A tale of two proteins: differential roles and regulation of Smad2 and Smad3 in TGF-beta signaling.J Cell Biochem. 2007 May 1;101(1):9-33. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21255. J Cell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17340614 Review.
Cited by
-
Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells (TREM)-2 Impairs Host Defense in Experimental Melioidosis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016 Jun 2;10(6):e0004747. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004747. eCollection 2016 Jun. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016. PMID: 27253382 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombocytopenia Impairs Host Defense Against Burkholderia pseudomallei (Melioidosis).J Infect Dis. 2019 Jan 29;219(4):648-659. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiy541. J Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30312422 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Toll-Like Receptor 5 (TLR5) in Experimental Melioidosis.Infect Immun. 2019 Jul 23;87(8):e00409-18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00409-18. Print 2019 Aug. Infect Immun. 2019. PMID: 31109950 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Expression Profile of Human Cytokines in Response to Burkholderia pseudomallei Infection.mSphere. 2017 Apr 19;2(2):e00121-17. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00121-17. eCollection 2017 Mar-Apr. mSphere. 2017. PMID: 28435890 Free PMC article.
-
TGFβ depletion does neither modulate acute E. coli-induced inflammatory immune responses nor impair the protective effect by chronic filarial infection.GMS Infect Dis. 2019 Nov 12;7:Doc04. doi: 10.3205/id000044. eCollection 2019. GMS Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31815088 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Currie BJ. 2003. Melioidosis: an important cause of pneumonia in residents of and travellers returned from endemic regions. Eur. Respir. J. 22:542–550 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

