Leptin protects host cells from Entamoeba histolytica cytotoxicity by a STAT3-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 22331430
- PMCID: PMC3347425
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.06140-11
Leptin protects host cells from Entamoeba histolytica cytotoxicity by a STAT3-dependent mechanism
Abstract
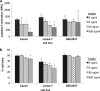
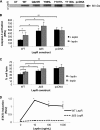
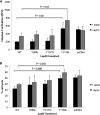
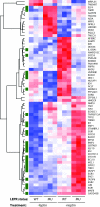
The adipocytokine leptin links nutritional status to immune function. Leptin signaling protects from amebiasis, but the molecular mechanism is not understood. We developed an in vitro model of ameba-host cell interaction to test the hypothesis that leptin prevents ameba-induced apoptosis in host epithelial cells. We demonstrated that activation of mammalian leptin signaling increased cellular resistance to amebic cytotoxicity, including caspase-3 activation. Exogenous expression of the leptin receptor conferred resistance in susceptible cells, and leptin stimulation enhanced protection. A series of leptin receptor signaling mutants showed that resistance to amebic cytotoxicity was dependent on activation of STAT3 but not the Src homology-2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatase (SHP-2) or STAT5. A common polymorphism in the leptin receptor (Q223R) that increases susceptibility to amebiasis in humans and mice was found to increase susceptibility to amebic cytotoxicity in single cells. The Q223R polymorphism also decreased leptin-dependent STAT3 activation by 21% relative to that of the wild-type (WT) receptor (P = 0.035), consistent with a central role of STAT3 signaling in protection. A subset of genes uniquely regulated by STAT3 in response to leptin was identified. Most notable were the TRIB1 and suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3) genes, which have opposing roles in the regulation of apoptosis. Overall apoptotic genes were highly enriched in this gene set (P < 1E-05), supporting the hypothesis that leptin regulation of host apoptotic genes via STAT3 is responsible for protection. This is the first demonstration of a mammalian signaling pathway that restricts amebic pathogenesis and represents an important advance in our mechanistic understanding of how leptin links nutrition and susceptibility to infection.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Leptin signaling in intestinal epithelium mediates resistance to enteric infection by Entamoeba histolytica.Mucosal Immunol. 2011 May;4(3):294-303. doi: 10.1038/mi.2010.76. Epub 2010 Dec 1. Mucosal Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21124310 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the leptin receptor Q223R polymorphism on the host transcriptome following infection with Entamoeba histolytica.Infect Immun. 2013 May;81(5):1460-70. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01383-12. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Infect Immun. 2013. PMID: 23429533 Free PMC article.
-
Degradation of the transcription factors NF-κB, STAT3, and STAT5 is involved in Entamoeba histolytica-induced cell death in Caco-2 colonic epithelial cells.Korean J Parasitol. 2014 Oct;52(5):459-69. doi: 10.3347/kjp.2014.52.5.459. Epub 2014 Oct 22. Korean J Parasitol. 2014. PMID: 25352693 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin and mucosal immunity.Mucosal Immunol. 2012 Sep;5(5):472-9. doi: 10.1038/mi.2012.40. Epub 2012 Jun 13. Mucosal Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22692456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leptin signaling protects the gut from Entamoeba histolytica infection.Gut Microbes. 2012 Jan-Feb;3(1):2-3. doi: 10.4161/gmic.19424. Epub 2012 Jan 1. Gut Microbes. 2012. PMID: 22356851 Review.
Cited by
-
Intestinal Infection of Candida albicans: Preventing the Formation of Biofilm by C. albicans and Protecting the Intestinal Epithelial Barrier.Front Microbiol. 2022 Feb 2;12:783010. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.783010. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35185813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intestinal parasites: Associations with intestinal and systemic inflammation.Parasite Immunol. 2018 Apr;40(4):e12518. doi: 10.1111/pim.12518. Epub 2018 Mar 4. Parasite Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29364525 Free PMC article.
-
Host Protective Mechanisms to Intestinal Amebiasis.Trends Parasitol. 2021 Feb;37(2):165-175. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2020.09.015. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Trends Parasitol. 2021. PMID: 33502317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxicological Evaluation of Kaempferol and Linearolactone as Treatments for Amoebic Liver Abscess Development in Mesocricetus auratus.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 2;25(19):10633. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910633. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408962 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian tribbles homologs at the crossroads of endoplasmic reticulum stress and Mammalian target of rapamycin pathways.Scientifica (Cairo). 2013;2013:750871. doi: 10.1155/2013/750871. Epub 2013 Dec 30. Scientifica (Cairo). 2013. PMID: 24490110 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banks AS, Davis SM, Bates SH, Myers MG., Jr 2000. Activation of downstream signals by the long form of the leptin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 275:14563–14572 - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. 1995. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. B (Methodol.) 57:289–300
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

