Mechanical stress-activated integrin α5β1 induces opening of connexin 43 hemichannels
- PMID: 22331870
- PMCID: PMC3295295
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1115967109
Mechanical stress-activated integrin α5β1 induces opening of connexin 43 hemichannels
Abstract
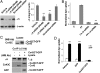
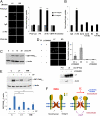
The connexin 43 (Cx43) hemichannel (HC) in the mechanosensory osteocytes is a major portal for the release of factors responsible for the anabolic effects of mechanical loading on bone formation and remodeling. However, little is known about how the Cx43 molecule responds to mechanical stimulation leading to the opening of the HC. Here, we demonstrate that integrin α5β1 interacts directly with Cx43 and that this interaction is required for mechanical stimulation-induced opening of the Cx43 HC. Direct mechanical perturbation via magnetic beads or conformational activation of integrin α5β1 leads to the opening of the Cx43 HC, and this role of the integrin is independent of its association with an extracellular fibronectin substrate. PI3K signaling is responsible for the shear stress-induced conformational activation of integrin α5β1 leading to the opening of the HC. These results identify an unconventional function of integrin that acts as a mechanical tether to induce opening of the HC and provide a mechanism connecting the effect of mechanical forces directly to anabolic function of the bone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Robling AG, Castillo AB, Turner CH. Biomechanical and molecular regulation of bone remodeling. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2006;8:455–498. - PubMed
-
- Alford AI, Jacobs CR, Donahue HJ. Oscillating fluid flow regulates gap junction communication in osteocytic MLO-Y4 cells by an ERK1/2 MAP kinase-dependent mechanism. Bone. 2003;33:64–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

