Inhibitor of streptokinase gene expression improves survival after group A streptococcus infection in mice
- PMID: 22331877
- PMCID: PMC3295313
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1201031109
Inhibitor of streptokinase gene expression improves survival after group A streptococcus infection in mice
Abstract
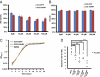
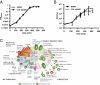
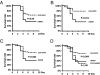
The widespread occurrence of antibiotic resistance among human pathogens is a major public health problem. Conventional antibiotics typically target bacterial killing or growth inhibition, resulting in strong selection for the development of antibiotic resistance. Alternative therapeutic approaches targeting microbial pathogenicity without inhibiting growth might minimize selection for resistant organisms. Compounds inhibiting gene expression of streptokinase (SK), a critical group A streptococcal (GAS) virulence factor, were identified through a high-throughput, growth-based screen on a library of 55,000 small molecules. The lead compound [Center for Chemical Genomics 2979 (CCG-2979)] and an analog (CCG-102487) were confirmed to also inhibit the production of active SK protein. Microarray analysis of GAS grown in the presence of CCG-102487 showed down-regulation of a number of important virulence factors in addition to SK, suggesting disruption of a general virulence gene regulatory network. CCG-2979 and CCG-102487 both enhanced granulocyte phagocytosis and killing of GAS in an in vitro assay, and CCG-2979 also protected mice from GAS-induced mortality in vivo. These data suggest that the class of compounds represented by CCG-2979 may be of therapeutic value for the treatment of GAS and potentially other gram-positive infections in humans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
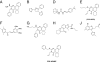
References
-
- Högberg LD, Heddini A, Cars O. The global need for effective antibiotics: Challenges and recent advances. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2010;31:509–515. - PubMed
-
- Hung DT, Shakhnovich EA, Pierson E, Mekalanos JJ. Small-molecule inhibitor of Vibrio cholerae virulence and intestinal colonization. Science. 2005;310:670–674. - PubMed
-
- Carapetis JR, Steer AC, Mulholland EK, Weber M. The global burden of group A streptococcal diseases. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005;5:685–694. - PubMed
-
- Bisno AL, Stevens DL. Streptococcal infections of skin and soft tissues. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:240–245. - PubMed
-
- Cole JN, Barnett TC, Nizet V, Walker MJ. Molecular insight into invasive group A streptococcal disease. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011;9:724–736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

