Colorectal and other cancer risks for carriers and noncarriers from families with a DNA mismatch repair gene mutation: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 22331944
- PMCID: PMC3341109
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2011.39.5590
Colorectal and other cancer risks for carriers and noncarriers from families with a DNA mismatch repair gene mutation: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Purpose: To determine whether cancer risks for carriers and noncarriers from families with a mismatch repair (MMR) gene mutation are increased above the risks of the general population.
Patients and methods: We prospectively followed a cohort of 446 unaffected carriers of an MMR gene mutation (MLH1, n = 161; MSH2, n = 222; MSH6, n = 47; and PMS2, n = 16) and 1,029 their unaffected relatives who did not carry a mutation every 5 years at recruitment centers of the Colon Cancer Family Registry. For comparison of cancer risk with the general population, we estimated country-, age-, and sex-specific standardized incidence ratios (SIRs) of cancer for carriers and noncarriers.
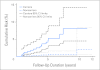
Results: Over a median follow-up of 5 years, mutation carriers had an increased risk of colorectal cancer (CRC; SIR, 20.48; 95% CI, 11.71 to 33.27; P < .001), endometrial cancer (SIR, 30.62; 95% CI, 11.24 to 66.64; P < .001), ovarian cancer (SIR, 18.81; 95% CI, 3.88 to 54.95; P < .001), renal cancer (SIR, 11.22; 95% CI, 2.31 to 32.79; P < .001), pancreatic cancer (SIR, 10.68; 95% CI, 2.68 to 47.70; P = .001), gastric cancer (SIR, 9.78; 95% CI, 1.18 to 35.30; P = .009), urinary bladder cancer (SIR, 9.51; 95% CI, 1.15 to 34.37; P = .009), and female breast cancer (SIR, 3.95; 95% CI, 1.59 to 8.13; P = .001). We found no evidence of their noncarrier relatives having an increased risk of any cancer, including CRC (SIR, 1.02; 95% CI, 0.33 to 2.39; P = .97).
Conclusion: We confirmed that carriers of an MMR gene mutation were at increased risk of a wide variety of cancers, including some cancers not previously recognized as being a result of MMR mutations, and found no evidence of an increased risk of cancer for their noncarrier relatives.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Järvinen HJ, Aarnio M, Mustonen H, et al. Controlled 15-year trial on screening for colorectal cancer in families with hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 2000;118:829–834. - PubMed
-
- de Jong AE, Hendriks YM, Kleibeuker JH, et al. Decrease in mortality in Lynch syndrome families because of surveillance. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:665–671. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

