Subjective cognition and amyloid deposition imaging: a Pittsburgh Compound B positron emission tomography study in normal elderly individuals
- PMID: 22332189
- PMCID: PMC4004919
- DOI: 10.1001/archneurol.2011.666
Subjective cognition and amyloid deposition imaging: a Pittsburgh Compound B positron emission tomography study in normal elderly individuals
Abstract
Objective: To study the relationship between subjective cognition and the neuropathological hallmark of Alzheimer disease (AD), amyloid-β (Aβ) deposition, using carbon 11-labeled Pittsburgh Compound B (PiB) positron emission tomography in normal elderly individuals.
Design: Cross-sectional analysis.
Subjects: Forty-eight cognitively normal elderly subjects (11 with high PiB uptake and 28 with low PiB uptake) were included. All underwent clinical and neuropsychological evaluations, magnetic resonance imaging, and positron emission tomography.
Setting: Berkeley Aging Cohort Study.
Main outcome measure: Relationship between PiB uptake and subjective cognition measures.
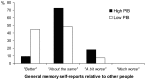
Results: Subjects with high PiB uptake showed significantly lower performance than those with low PiB uptake on an episodic memory measure and were less confident about their general memory abilities when required to evaluate themselves relative to other people of the same age. High and low PiB uptake groups did not differ on the accuracy of their cognitive self-reports compared with objective cognitive performance. General memory self-reports from the whole group were significantly correlated with regional PiB uptake in the right medial prefrontal cortex and anterior cingulate cortex and in the right precuneus and posterior cingulate cortex. Reduced confidence about memory abilities was associated with greater PiB uptake in these brain regions. All results were independent of demographic variables and depressive affects.
Conclusions: A decrease of self-confidence about memory abilities in cognitively normal elderly subjects may be related to the neuropathological hallmark of AD measured with PiB-positron emission tomography. Subjective cognitive impairment may represent a very early clinical manifestation of AD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of lifetime cognitive engagement and low β-amyloid deposition.Arch Neurol. 2012 May;69(5):623-29. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2011.2748. Arch Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22271235 Free PMC article.
-
β-Amyloid affects frontal and posterior brain networks in normal aging.Neuroimage. 2011 Feb 1;54(3):1887-95. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.10.027. Epub 2010 Oct 18. Neuroimage. 2011. PMID: 20965254 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of amyloid β on cognitive decline is modulated by neural integrity in cognitively normal elderly.Alzheimers Dement. 2013 Nov;9(6):687-698.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2012.10.012. Epub 2013 Mar 7. Alzheimers Dement. 2013. PMID: 23474040 Free PMC article.
-
PET imaging of brain amyloid in dementia: a review.Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2011 Oct;26(10):991-9. doi: 10.1002/gps.2640. Epub 2010 Dec 28. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21905095 Review.
-
Amyloid imaging in aging and dementia: testing the amyloid hypothesis in vivo.Behav Neurol. 2009;21(1):117-28. doi: 10.3233/BEN-2009-0232. Behav Neurol. 2009. PMID: 19847050 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of serum Apolipoprotein B with cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of Alzheimer's pathology.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2020 Oct;7(10):1766-1778. doi: 10.1002/acn3.51153. Epub 2020 Sep 10. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32910550 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning based on the multimodal connectome can predict the preclinical stage of Alzheimer's disease: a preliminary study.Eur Radiol. 2022 Jan;32(1):448-459. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08080-9. Epub 2021 Jun 10. Eur Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34109489
-
Refining the metamemory in adulthood questionnaire: a 20-item version of change and capacity designed for research and clinical settings.Aging Ment Health. 2020 Jul;24(7):1054-1063. doi: 10.1080/13607863.2019.1594160. Epub 2019 Apr 7. Aging Ment Health. 2020. PMID: 30957531 Free PMC article.
-
The meta-memory ratio: a new cohort-independent way to measure cognitive awareness in asymptomatic individuals at risk for Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2020 May 14;12(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13195-020-00626-1. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32408882 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid imaging in cognitively normal individuals, at-risk populations and preclinical Alzheimer's disease.Neuroimage Clin. 2013 Mar 5;2:356-65. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2013.02.006. eCollection 2013. Neuroimage Clin. 2013. PMID: 24179789 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gauthier S, Reisberg B, Zaudig M, et al. Mild cognitive impairment. Lancet. 2006;367(9518):1262–1270. - PubMed
-
- Jessen F, Wiese B, Bachmann C, et al. Prediction of dementia by subjective memory impairment: effects of severity and temporal association with cognitive impairment. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010;67(4):414–422. - PubMed
-
- Reisberg B, Prichep L, Mosconi L, et al. The pre-mild cognitive impairment, subjective cognitive impairment stage of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2008;4(1 Suppl 1):S98–S108. - PubMed
-
- Jonker C, Geerlings MI, Schmand B. Are memory complaints predictive for dementia? A review of clinical and population-based studies. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2000;15(11):983–991. - PubMed