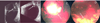
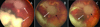
Residual intraretinal retinoblastoma after chemoreduction failure
- PMID: 22332223
- PMCID: PMC3417053
- DOI: 10.1001/archopthalmol.2011.1588
Residual intraretinal retinoblastoma after chemoreduction failure
Figures

Similar articles
-
Histopathologic findings in eyes with retinoblastoma treated only with chemoreduction.Arch Ophthalmol. 2003 Aug;121(8):1125-31. doi: 10.1001/archopht.121.8.1125. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003. PMID: 12912690
-
Chemoreduction for nonvisualized retinoblastoma hidden behind dense cataract.Can J Ophthalmol. 2010 Oct;45(5):539-40. doi: 10.3129/i10-025. Can J Ophthalmol. 2010. PMID: 20648072 No abstract available.
-
Causes of chemoreduction failure in retinoblastoma and analysis of associated factors leading to eventual treatment with external beam radiotherapy and enucleation.Ophthalmology. 2004 Oct;111(10):1917-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2004.04.016. Ophthalmology. 2004. PMID: 15465557
-
Retinoblastoma: evidence for postenucleation adjuvant chemotherapy.Int Ophthalmol Clin. 2015 Winter;55(1):77-96. doi: 10.1097/IIO.0000000000000048. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 2015. PMID: 25436495 Review. No abstract available.
-
Current management strategies for intraocular retinoblastoma.Drugs. 2007;67(15):2173-85. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200767150-00005. Drugs. 2007. PMID: 17927283 Review.
Cited by
-
Retinoblastoma. Fifty years of progress. The LXXI Edward Jackson Memorial Lecture.Am J Ophthalmol. 2014 Nov;158(5):875-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2014.07.025. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Am J Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 25065496 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shields CL, Ghassemi F, Tuncer S, Thangappan A, Shields JA. Clinical spectrum of diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma in 34 consecutive eyes. Ophthalmology. 2008;115:2253–2258. - PubMed
-
- Foster BS, Mukai S. Intraocular retinoblastoma presenting as ocular and orbital inflammation. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1996;36:153–160. - PubMed
-
- Tapper D, Langer R, Bellows AR, Folkman J. Angiogenesis capacity as a diagnostic marker for human eye tumors. Surgery. 1979;86:36–40. - PubMed
-
- Pina Y, Boutrid H, Schefler A, et al. Blood vessel maturation in retinoblastoma tumors: spatial distribution of neovessels and mature vessels and its impact on ocular treatment. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009;50:1020–1024. - PubMed
-
- Seigel GM, Campbell LM, Narayan M, Gonzalez-Fernandez F. Cancer stem cell characteristics in retinoblastoma. Mol Vis. 2005;11:729–737. - PubMed

