Thermodynamic signature of DNA damage: characterization of DNA with a 5-hydroxy-2'-deoxycytidine·2'-deoxyguanosine base pair
- PMID: 22332945
- PMCID: PMC3319050
- DOI: 10.1021/bi3000269
Thermodynamic signature of DNA damage: characterization of DNA with a 5-hydroxy-2'-deoxycytidine·2'-deoxyguanosine base pair
Abstract
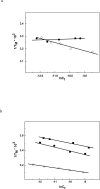
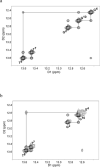
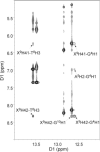
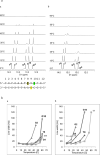
Oxidation of DNA due to exposure to reactive oxygen species is a major source of DNA damage. One of the oxidation lesions formed, 5-hydroxy-2'-deoxycytidine, has been shown to miscode by some replicative DNA polymerases but not by error prone polymerases capable of translesion synthesis. The 5-hydroxy-2'-deoxycytidine lesion is repaired by DNA glycosylases that require the 5-hydroxycytidine base to be extrahelical so it can enter into the enzyme's active site where it is excised off the DNA backbone to afford an abasic site. The thermodynamic and nuclear magnetic resonance results presented here describe the effect of a 5-hydroxy-2'-deoxycytidine·2'-deoxyguanosine base pair on the stability of two different DNA duplexes. The results demonstrate that the lesion is highly destabilizing and that the energy barrier for the unstacking of 5-hydroxy-2'-deoxycytidine from the DNA duplex may be low. This could provide a thermodynamic mode of adduct identification by DNA glycosylases that requires the lesion to be extrahelical.
Figures




References
-
- Imlay JA, Linn S. DNA damage and oxygen radical toxicity. Science. 1988;240:1302–1309. - PubMed
-
- O'Brien PJ. Radical formation during the peroxidase catalyzed metabolism of carcinogens and xenobiotics: the reactivity of these radicals with GSH, DNA, and unsaturated lipid. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1988;4:169–183. - PubMed
-
- von Sonntag C. The chemistry of free-radical-mediated DNA damage. Basic Life Sci. 1991;58:287–317. - PubMed
-
- Dizdaroglu M. Chemical determination of free radical-induced damage to DNA. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1991;10:225–242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

