PANDAseq: paired-end assembler for illumina sequences
- PMID: 22333067
- PMCID: PMC3471323
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-31
PANDAseq: paired-end assembler for illumina sequences
Abstract
Background: Illumina paired-end reads are used to analyse microbial communities by targeting amplicons of the 16S rRNA gene. Publicly available tools are needed to assemble overlapping paired-end reads while correcting mismatches and uncalled bases; many errors could be corrected to obtain higher sequence yields using quality information.
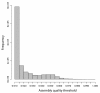
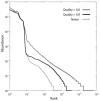
Results: PANDAseq assembles paired-end reads rapidly and with the correction of most errors. Uncertain error corrections come from reads with many low-quality bases identified by upstream processing. Benchmarks were done using real error masks on simulated data, a pure source template, and a pooled template of genomic DNA from known organisms. PANDAseq assembled reads more rapidly and with reduced error incorporation compared to alternative methods.
Conclusions: PANDAseq rapidly assembles sequences and scales to billions of paired-end reads. Assembly of control libraries showed a 4-50% increase in the number of assembled sequences over naïve assembly with negligible loss of "good" sequence.
Figures


References
-
- Bartram AK, Lynch MDJ, Stearns JC, Moreno-Hagelsieb G, Neufeld JD. Generation of multimillion-sequence 16S rRNA gene libraries from complex microbial communities by assembling paired-end Illumina reads. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011;77:3846–3852. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02772-10. http://aem.asm.org/cgi/content/abstract/77/11/3846 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Degnan PH, Ochman H. Illumina-based analysis of microbial community diversity. ISME J. 2011. http://www.nature.com/ismej/journal/v6/n1/full/ismej201174a.html - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D, Lozupone CA, Turnbaugh PJ, Fierer N, Knight R. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108(Suppl 1):4516–4522. http://genomebiology.com/2011/12/5/R50 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

