miRNAs versus oncogenes: the power of social networking
- PMID: 22333973
- PMCID: PMC3293632
- DOI: 10.1038/msb.2012.2
miRNAs versus oncogenes: the power of social networking
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Figures
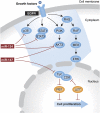
Comment on
-
Global microRNA level regulation of EGFR-driven cell-cycle protein network in breast cancer.Mol Syst Biol. 2012 Feb 14;8:570. doi: 10.1038/msb.2011.100. Mol Syst Biol. 2012. PMID: 22333974 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Global microRNA level regulation of EGFR-driven cell-cycle protein network in breast cancer.Mol Syst Biol. 2012 Feb 14;8:570. doi: 10.1038/msb.2011.100. Mol Syst Biol. 2012. PMID: 22333974 Free PMC article.
-
A working model for the time sequence of genetic changes in breast tumorigenesis.J Am Coll Surg. 2002 Feb;194(2):202-16. doi: 10.1016/s1072-7515(01)01108-5. J Am Coll Surg. 2002. PMID: 11848636 Review. No abstract available.
-
MicroRNA-101 inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting EYA1 in breast cancer.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Jun;37(6):1643-51. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2557. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27082308
-
The lncRNA GATA3-AS1/miR-495-3p/CENPU axis predicts poor prognosis of breast cancer via the PLK1 signaling pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Apr 26;13(10):13663-13679. doi: 10.18632/aging.202909. Epub 2021 Apr 26. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33902008 Free PMC article.
-
The potential of miRNAs for diagnosis, treatment and monitoring of breast cancer.Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 2016;245:S34-9. doi: 10.1080/00365513.2016.1208444. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 2016. PMID: 27435502 Review.
Cited by
-
Systems approach for the selection of micro-RNAs as therapeutic biomarkers of anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody treatment in colorectal cancer.Sci Rep. 2015 Jan 27;5:8013. doi: 10.1038/srep08013. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25622824 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin resistant MDA-MB-468 cells exhibit EMT-like phenotype and increased migration capacity.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jul;49(7):5973-5984. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07381-6. Epub 2022 Mar 30. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35355210
-
MicroRNA 16 modulates epithelial sodium channel in human alveolar epithelial cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Sep 21;426(2):203-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.08.063. Epub 2012 Aug 23. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22940131 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating sequence, expression and interaction data to determine condition-specific miRNA regulation.Bioinformatics. 2013 Jul 1;29(13):i89-97. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt231. Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23813013 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic anti-tumor effect of paclitaxel and miR-34a combined with ultrasound microbubbles on cervical cancer in vivo and in vitro.Clin Transl Oncol. 2020 Jan;22(1):60-69. doi: 10.1007/s12094-019-02131-w. Epub 2019 May 15. Clin Transl Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31093891
References
-
- Avraham R, Sas-Chen A, Manor O, Steinfeld I, Shalgi R, Tarcic G, Bossel N, Zeisel A, Amit I, Zwang Y, Enerly E, Russnes HG, Biagioni F, Mottolese M, Strano S, Blandino G, Borresen-Dale AL, Pilpel Y, Yakhini Z, Segal E et al. (2010) EGF decreases the abundance of microRNAs that restrain oncogenic transcription factors. Sci Signal 3: ra43. - PubMed
-
- Bueno MJ, Gomez de Cedron M, Gomez-Lopez G, Perez de Castro I, Di Lisio L, Montes-Moreno S, Martinez N, Guerrero M, Sanchez-Martinez R, Santos J, Pisano DG, Piris MA, Fernandez-Piqueras J, Malumbres M (2011) Combinatorial effects of microRNAs to suppress the Myc oncogenic pathway. Blood 117: 6255–6266 - PubMed
-
- Bueno MJ, Malumbres M (2011) MicroRNAs and the cell cycle. Biochim Biophys Acta 1812: 592–601 - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Guo X, Zhang H, Xiang Y, Chen J, Yin Y, Cai X, Wang K, Wang G, Ba Y, Zhu L, Wang J, Yang R, Zhang Y, Ren Z, Zen K, Zhang J, Zhang CY (2009) Role of miR-143 targeting KRAS in colorectal tumorigenesis. Oncogene 28: 1385–1392 - PubMed
-
- Garofalo M, Romano G, Di Leva G, Nuovo G, Jeon YJ, Ngankeu A, Sun J, Lovat F, Alder H, Condorelli G, Engelman JA, Ono M, Rho JK, Cascione L, Volinia S, Nephew KP, Croce CM (2011) EGFR and MET receptor tyrosine kinase-altered microRNA expression induces tumorigenesis and gefitinib resistance in lung cancers. Nat Med 18: 74–82 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

