Evaluation of the antiproliferative activity of the leaves from Arctium lappa by a bioassay-guided fractionation
- PMID: 22334063
- PMCID: PMC6268082
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules17021852
Evaluation of the antiproliferative activity of the leaves from Arctium lappa by a bioassay-guided fractionation
Abstract
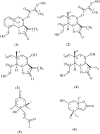
Arctium lappa L. (Asteraceae) is used in folk medicine around the World, and shows several kinds of biological activity, particularly in vitro antitumor activity in different cell lines. This study evaluated the antiproliferative activity of the crude extract, semipurified fractions, and isolated compounds from the leaves of A. lappa, through bioassay-guided testing in Caco-2 cells. The crude extract was obtained with a 50% hydroethanolic extract and then partitioned with hexane, ethyl acetate, and n-butanol. The ethyl-acetate fraction (EAF) showed antiproliferative activity. This fraction was subjected to sequential column chromatography over silica gel to afford onopordopicrin (1), mixtures of 1 with dehydromelitensin-8-(4'-hydroxymethacrylate) (2), a mixture of 2 with dehydromelitensin (3), mixture of 1 with melitensin (4), dehydrovomifoliol (5), and loliolide (6). The compounds were identified by spectroscopic methods (NMR, MS) and comparison with literature data. This is the first description of compounds 2-5 from this species. The compounds tested in Caco-2 cells showed the following CC(50) (µg/mL) values: 1: 19.7 ± 3.4, 1 with 2: 24.6 ± 1.5, 2 with 3: 27 ± 11.7, 1 with 4: 42 ± 13.1, 6 30 ± 6.2; compound 5 showed no activity.
Figures
References
-
- Predes F.S., Monteiro J.C., Paula T.A.R., Matta S.L.P. Evaluation of rat testes treated with Arctium lappa L: Morphometric study. Braz. J. Morphol. Sci. 2007;24:112–117.
-
- Foldeak S., Dombradi G.A. Tumor-growth inhibiting substances of plant origin. I. Isolation of the active principle of Arctium lappa. Acta Phys. Chem. 1964;10:91–93.
-
- Ming D.S., Guns E., Eberding A., Towers N.G.H. Isolation and characterization of compounds with anti-prostate cancer activity from Arctium lappa L. using bioactivity-guided fractionation. Pharm. Biol. 2004;42:44–48. doi: 10.1080/13880200490505474. - DOI
-
- Uchiyama Y., Tagami J., Kamisuki S., Kasai N., Oshige M., Chiku H., Ibe S., Koiwai O., Sugawara F., Sakagushi K. Selective inhibitors of terminal deoxyribonucleotidyltransferase (TdT): Baicalin and genistin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2005;1725:298–304. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2005.06.017. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases