CPEB-mediated ZO-1 mRNA localization is required for epithelial tight-junction assembly and cell polarity
- PMID: 22334078
- PMCID: PMC4334452
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms1678
CPEB-mediated ZO-1 mRNA localization is required for epithelial tight-junction assembly and cell polarity
Abstract
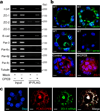
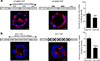
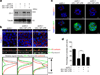
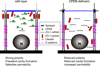
CPEB is a translational regulatory sequence-specific RNA-binding protein that controls germ cell development. Here we show that CPEB heterozygous female mice are fertile but contain disorganized mammary epithelial cells, in which zonal occludens-1 and claudin-3, apical tight-junction proteins, are mislocalized. CPEB depletion from mammary epithelial cells disrupts zonal occludens-1 apical localization and tight-junction distribution; conversely, ectopic expression of CPEB enhances zonal occludens-1 localization. CPEB and zonal occludens-1 mRNA are co-localized apically and zonal occludens-1 3' untranslated region-binding sites for CPEB are necessary for RNA localization. In a three-dimensional culture system that models lumen-containing mammary ducts, depletion of CPEB or zonal occludens-1 impairs central cavity formation, indicating a loss of cell polarity. Cavity formation in zonal occludens-1-depleted cells is rescued when they are transduced with zonal occludens-1 mRNA containing, but not lacking, CPEB-binding sites. Our data demonstrate that CPEB-mediated zonal occludens-1 mRNA localization is essential for tight-junction assembly and mammary epithelial cell polarity.
Figures
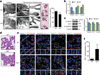
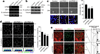
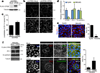
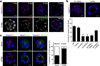
Comment in
-
Cell polarity: CPEB gets tight with junctions.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Feb 23;13(3):138. doi: 10.1038/nrm3295. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22358323 No abstract available.
References
-
- St Johnston D, Ahringer J. Cell polarity in eggs and epithelia: parallels and diversity. Cell. 2010;141:757–774. - PubMed
-
- Meignin C, Davis I. Transmitting the message: intracellular mRNA localization. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010;22:112–119. - PubMed
-
- Czaplinski K, Singer RH. Pathways for mRNA localization in the cytoplasm. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006;31:687–693. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

