Crystal structure of vinculin in complex with vinculin binding site 50 (VBS50), the integrin binding site 2 (IBS2) of talin
- PMID: 22334306
- PMCID: PMC3375758
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.2041
Crystal structure of vinculin in complex with vinculin binding site 50 (VBS50), the integrin binding site 2 (IBS2) of talin
Abstract
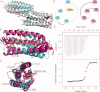
The cytoskeletal protein talin activates integrin receptors by binding of its FERM domain to the cytoplasmic tail of β-integrin. Talin also couples integrins to the actin cytoskeleton, largely by binding to and activating the cytoskeletal protein vinculin, which binds to F-actin through the agency of its five-helix bundle tail (Vt) domain. Talin activates vinculin by means of buried amphipathic α-helices coined vinculin binding sites (VBSs) that reside within numerous four- and five-helix bundle domains that comprise the central talin rod, which are released from their buried locales by means of mechanical tension on the integrin:talin complex. In turn, these VBSs bind to the N-terminal seven-helix bundle (Vh1) domain of vinculin, creating an entirely new helix bundle that severs its head-tail interactions. Interestingly, talin harbors a second integrin binding site coined IBS2 that consists of two five-helix bundle domains that also contain a VBS (VBS50). Here we report the crystal structure of VBS50 in complex with vinculin at 2.3 Å resolution and show that intramolecular interactions of VBS50 within IBS2 are much more extensive versus its interactions with vinculin. Indeed, the IBS2-vinculin interaction only occurs at physiological temperature and the affinity of VBS50 for vinculin is about 30 times less than other VBSs. The data support a model where integrin binding destabilizes IBS2 to allow it to bind to vinculin.
Copyright © 2012 The Protein Society.
Figures
References
-
- Critchley DR. Biochemical and structural properties of the integrin-associated cytoskeletal protein talin. Annual Rev Biophys. 2009;38:235–254. - PubMed
-
- Calderwood DA. Integrin activation. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:657–666. - PubMed
-
- Calderwood DA, Zent R, Grant R, Rees DJ, Hynes RO, Ginsberg MH. The Talin head domain binds to integrin β subunit cytoplasmic tails and regulates integrin activation. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:28071–28074. - PubMed
-
- Moes M, Rodius S, Coleman SJ, Monkley SJ, Goormaghtigh E, Tremuth L, Kox C, van der Holst PP, Critchley DR, Kieffer N. The integrin binding site 2 (IBS2) in the talin rod domain is essential for linking integrin β subunits to the cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:17280–17288. - PubMed
-
- Gingras AR, Ziegler WH, Bobkov AA, Joyce MG, Fasci D, Himmel M, Rothemund S, Ritter A, Grossmann JG, Patel B, Bate N, Goult BT, Emsley J, Barsukov IL, Roberts GC, Liddington RC, Ginsberg MH, Critchley DR. Structural determinants of integrin binding to the talin rod. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:8866–8876. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

