Accurate measurement of the relative abundance of different DNA species in complex DNA mixtures
- PMID: 22334570
- PMCID: PMC3372371
- DOI: 10.1093/dnares/dss002
Accurate measurement of the relative abundance of different DNA species in complex DNA mixtures
Abstract
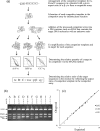
A molecular tool that can compare the abundances of different DNA sequences is necessary for comparing intergenic or interspecific gene expression. We devised and verified such a tool using a quantitative competitive polymerase chain reaction approach. For this approach, we adapted a competitor array, an artificially made plasmid DNA in which all the competitor templates for the target DNAs are arranged with a defined ratio, and melting analysis for allele quantitation for accurate quantitation of the fractional ratios of competitively amplified DNAs. Assays on two sets of DNA mixtures with explicitly known compositional structures of the test sequences were performed. The resultant average relative errors of 0.059 and 0.021 emphasize the highly accurate nature of this method. Furthermore, the method's capability of obtaining biological data is demonstrated by the fact that it can illustrate the tissue-specific quantitative expression signatures of the three housekeeping genes G6pdx, Ubc, and Rps27 by using the forms of the relative abundances of their transcripts, and the differential preferences of Igf2 enhancers for each of the multiple Igf2 promoters for the transcription.
Figures


References
-
- Schena M., Shalon D., Davis R.W., Brown P.O. Quantitative monitoring of gene expression patterns with a complementary DNA microarray. Science. 1995;270:467–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

