Carbon monoxide modulates apoptosis by reinforcing oxidative metabolism in astrocytes: role of Bcl-2
- PMID: 22334654
- PMCID: PMC3322847
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.306738
Carbon monoxide modulates apoptosis by reinforcing oxidative metabolism in astrocytes: role of Bcl-2
Abstract
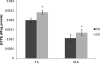
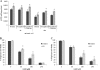
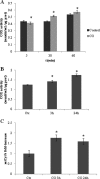
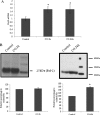
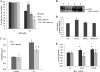
Modulation of cerebral cell metabolism for improving the outcome of hypoxia-ischemia and reperfusion is a strategy yet to be explored. Because carbon monoxide (CO) is known to prevent cerebral cell death; herein the role of CO in the modulation of astrocytic metabolism, in particular, at the level of mitochondria was investigated. Low concentrations of CO partially inhibited oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in astrocytes, by preventing caspase-3 activation, mitochondrial potential depolarization, and plasmatic membrane permeability. CO exposure enhanced intracellular ATP generation, which was accompanied by an increase on specific oxygen consumption, a decrease on lactate production, and a reduction of glucose use, indicating an improvement of oxidative phosphorylation. Accordingly, CO increased cytochrome c oxidase (COX) enzymatic specific activity and stimulated mitochondrial biogenesis. In astrocytes, COX interacts with Bcl-2, which was verified by immunoprecipitation; this interaction is superior after 24 h of CO treatment. Furthermore, CO enhanced Bcl-2 expression in astrocytes. By silencing Bcl-2 expression with siRNA transfection, CO effects in astrocytes were prevented, namely: (i) inhibition of apoptosis, (ii) increase on ATP generation, (iii) stimulation of COX activity, and (iv) mitochondrial biogenesis. Thus, Bcl-2 expression is crucial for CO modulation of oxidative metabolism and for conferring cytoprotection. In conclusion, CO protects astrocytes against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis by improving metabolism functioning, particularly mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation.
Figures
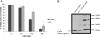
References
-
- Motterlini R., Otterbein L. E. (2010) The therapeutic potential of carbon monoxide. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 9, 728–743 - PubMed
-
- Soares M. P., Bach F. H. (2009) Heme oxygenase-1: From biology to therapeutic potential. Trends Mol. Med. 15, 50–58 - PubMed
-
- Bannenberg G. L., Vieira H. L. (2009) Therapeutic applications of the gaseous mediators carbon monoxide and hydrogen sulfide. Expert. Opin. Ther. Pat. 19, 663–682 - PubMed
-
- Ryter S. W., Alam J., Choi A. M. (2006) Heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide: From basic science to therapeutic applications. Physiol. Rev. 86, 583–650 - PubMed
-
- Zhang X., Shan P., Alam J., Davis R. J., Flavell R. A., Lee P. J. (2003) Carbon monoxide modulates Fas/Fas ligand, caspases, and Bcl-2 family proteins via the p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway during ischemia-reperfusion lung injury. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 22061–22070 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

