Phosphorylation of ORC2 protein dissociates origin recognition complex from chromatin and replication origins
- PMID: 22334659
- PMCID: PMC3320937
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.338467
Phosphorylation of ORC2 protein dissociates origin recognition complex from chromatin and replication origins
Abstract
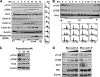
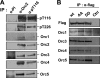
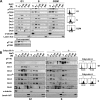
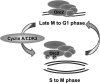
During the late M to the G(1) phase of the cell cycle, the origin recognition complex (ORC) binds to the replication origin, leading to the assembly of the prereplicative complex for subsequent initiation of eukaryotic chromosome replication. We found that the cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation of human ORC2, one of the six subunits of ORC, dissociates ORC2, -3, -4, and -5 (ORC2-5) subunits from chromatin and replication origins. Phosphorylation at Thr-116 and Thr-226 of ORC2 occurs by cyclin-dependent kinase during the S phase and is maintained until the M phase. Phosphorylation of ORC2 at Thr-116 and Thr-226 dissociated the ORC2-5 from chromatin. Consistent with this, the phosphomimetic ORC2 protein exhibited defective binding to replication origins as well as to chromatin, whereas the phosphodefective protein persisted in binding throughout the cell cycle. These results suggest that the phosphorylation of ORC2 dissociates ORC from chromatin and replication origins and inhibits binding of ORC to newly replicated DNA.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dephosphorylation of Orc2 by protein phosphatase 1 promotes the binding of the origin recognition complex to chromatin.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Jun 13;448(4):385-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.04.109. Epub 2014 Apr 30. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 24792176
-
Protein phosphatase 1 dephosphorylates Orc2.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 May 9;447(3):437-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.04.029. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 24732362
-
A human cancer cell line initiates DNA replication normally in the absence of ORC5 and ORC2 proteins.J Biol Chem. 2020 Dec 11;295(50):16949-16959. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015450. Epub 2020 Sep 28. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32989049 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple functions of the origin recognition complex.Int Rev Cytol. 2007;256:69-109. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7696(07)56003-1. Int Rev Cytol. 2007. PMID: 17241905 Review.
-
Stepwise assembly of initiation complexes at budding yeast replication origins during the cell cycle.J Cell Sci Suppl. 1995;19:67-72. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1995.supplement_19.9. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1995. PMID: 8655649 Review.
Cited by
-
De novo characterization of the spleen transcriptome of the large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) and analysis of the immune relevant genes and pathways involved in the antiviral response.PLoS One. 2014 May 12;9(5):e97471. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097471. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24820969 Free PMC article.
-
Links between DNA Replication, Stem Cells and Cancer.Genes (Basel). 2017 Jan 25;8(2):45. doi: 10.3390/genes8020045. Genes (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28125050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SCF(Cyclin F)-dependent degradation of CDC6 suppresses DNA re-replication.Nat Commun. 2016 Jan 28;7:10530. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10530. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 26818844 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of Orc6 During Mitosis Regulates DNA Replication and Ribosome Biogenesis.Mol Cell Biol. 2024;44(7):289-301. doi: 10.1080/10985549.2024.2356880. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38867464 Free PMC article.
-
The MCM8-MCM9 complex promotes RAD51 recruitment at DNA damage sites to facilitate homologous recombination.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Apr;33(8):1632-44. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01503-12. Epub 2013 Feb 11. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23401855 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bell S. P., Dutta A. (2002) DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71, 333–374 - PubMed
-
- Diffley J. F. (2004) Regulation of early events in chromosome replication. Curr. Biol. 14, R778–R786 - PubMed
-
- DePamphilis M. L., Blow J. J., Ghosh S., Saha T., Noguchi K., Vassilev A. (2006) Regulating the licensing of DNA replication origins in metazoa. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 18, 231–239 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

