Phosphorylation of ORC2 protein dissociates origin recognition complex from chromatin and replication origins
- PMID: 22334659
- PMCID: PMC3320937
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.338467
Phosphorylation of ORC2 protein dissociates origin recognition complex from chromatin and replication origins
Abstract
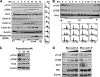
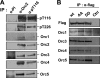
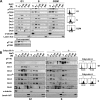
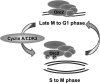
During the late M to the G(1) phase of the cell cycle, the origin recognition complex (ORC) binds to the replication origin, leading to the assembly of the prereplicative complex for subsequent initiation of eukaryotic chromosome replication. We found that the cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation of human ORC2, one of the six subunits of ORC, dissociates ORC2, -3, -4, and -5 (ORC2-5) subunits from chromatin and replication origins. Phosphorylation at Thr-116 and Thr-226 of ORC2 occurs by cyclin-dependent kinase during the S phase and is maintained until the M phase. Phosphorylation of ORC2 at Thr-116 and Thr-226 dissociated the ORC2-5 from chromatin. Consistent with this, the phosphomimetic ORC2 protein exhibited defective binding to replication origins as well as to chromatin, whereas the phosphodefective protein persisted in binding throughout the cell cycle. These results suggest that the phosphorylation of ORC2 dissociates ORC from chromatin and replication origins and inhibits binding of ORC to newly replicated DNA.
Figures


References
-
- Bell S. P., Dutta A. (2002) DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71, 333–374 - PubMed
-
- Diffley J. F. (2004) Regulation of early events in chromosome replication. Curr. Biol. 14, R778–R786 - PubMed
-
- DePamphilis M. L., Blow J. J., Ghosh S., Saha T., Noguchi K., Vassilev A. (2006) Regulating the licensing of DNA replication origins in metazoa. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 18, 231–239 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

