A detour for yeast oxysterol binding proteins
- PMID: 22334669
- PMCID: PMC3322883
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R111.338400
A detour for yeast oxysterol binding proteins
Abstract
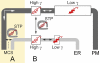
Oxysterol binding protein-related proteins, including the yeast proteins encoded by the OSH gene family (OSH1-OSH7), are implicated in the non-vesicular transfer of sterols between intracellular membranes and the plasma membrane. In light of recent studies, we revisited the proposal that Osh proteins are sterol transfer proteins and present new models consistent with known Osh protein functions. These models focus on the role of Osh proteins as sterol-dependent regulators of phosphoinositide and sphingolipid pathways. In contrast to their posited role as non-vesicular sterol transfer proteins, we propose that Osh proteins coordinate lipid signaling and membrane reorganization with the assembly of tethering complexes to promote molecular exchanges at membrane contact sites.
Figures

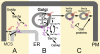
References
-
- Lingwood D., Simons K. (2010) Lipid rafts as a membrane-organizing principle. Science 327, 46–50 - PubMed
-
- Urbani L., Simoni R. D. (1990) Cholesterol and vesicular stomatitis virus G protein take separate routes from the endoplasmic reticulum to the plasma membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 1919–1923 - PubMed
-
- Baumann N. A., Sullivan D. P., Ohvo-Rekilä H., Simonot C., Pottekat A., Klaassen Z., Beh C. T., Menon A. K. (2005) Transport of newly synthesized sterol to the sterol-enriched plasma membrane occurs via non-vesicular equilibration. Biochemistry 44, 5816–5826 - PubMed
-
- Maxfield F. R., Menon A. K. (2006) Intracellular sterol transport and distribution. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 18, 379–385 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

