Synergistic and multidimensional regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 expression by transforming growth factor type β and epidermal growth factor
- PMID: 22334677
- PMCID: PMC3321001
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.338079
Synergistic and multidimensional regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 expression by transforming growth factor type β and epidermal growth factor
Abstract
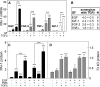
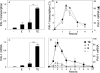
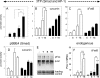
The major physiological inhibitor of plasminogen activator, type I plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1), controls blood clotting and tissue remodeling events that involve cell migration. Transforming growth factor type β (TGFβ) and epidermal growth factor (EGF) interact synergistically to increase PAI-1 mRNA and protein levels in human HepG2 and mink Mv1Lu cells. Other growth factors that activate tyrosine kinase receptors can substitute for EGF. EGF and TGFβ regulate PAI-1 by synergistically activating transcription, which is further amplified by a decrease in the rate of mRNA degradation, the latter being regulated only by EGF. The combined effect of transcriptional activation and mRNA stabilization results in a rapid 2-order of magnitude increase in the level of PAI-1. TGFβ also increases the sensitivity of the cells to EGF, thereby recruiting the cooperation of EGF at lower than normally effective concentrations. The contribution of EGF to the regulation of PAI-1 involves the MAPK pathway, and the synergistic interface with the TGFβ pathway is downstream of MEK1/2 and involves phosphorylation of neither ERK1/2 nor Smad2/3. Synergism requires the presence of both Smad and AP-1 recognition sites in the promoter. This work demonstrates the existence of a multidimensional cellular mechanism by which EGF and TGFβ are able to promote large and rapid changes in PAI-1 expression.
Figures


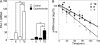
Similar articles
-
Opposite and independent actions of cyclic AMP and transforming growth factor beta in the regulation of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor expression.Biochem J. 1992 Nov 1;287 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):855-62. doi: 10.1042/bj2870855. Biochem J. 1992. PMID: 1332686 Free PMC article.
-
Differential mechanisms of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene activation by transforming growth factor-beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in endothelial cells.Thromb Haemost. 2001 Dec;86(6):1563-72. Thromb Haemost. 2001. PMID: 11776328
-
Differential regulation of the plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) gene expression by growth factors and progesterone in human endometrial stromal cells.Mol Hum Reprod. 1997 Sep;3(9):781-7. doi: 10.1093/molehr/3.9.781. Mol Hum Reprod. 1997. PMID: 9358004
-
Integration of non-SMAD and SMAD signaling in TGF-beta1-induced plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 gene expression in vascular smooth muscle cells.Thromb Haemost. 2008 Dec;100(6):976-83. Thromb Haemost. 2008. PMID: 19132220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation of the plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1--with an emphasis on negative regulation.Thromb Haemost. 2008 Dec;100(6):1007-13. Thromb Haemost. 2008. PMID: 19132223 Review.
Cited by
-
Transforming growth factor-beta signaling leads to uPA/PAI-1 activation and metastasis: a study on human breast cancer tissues.Pathol Oncol Res. 2014 Jul;20(3):727-32. doi: 10.1007/s12253-014-9753-2. Epub 2014 Mar 9. Pathol Oncol Res. 2014. PMID: 24610082
-
Follistatin N terminus differentially regulates muscle size and fat in vivo.Exp Mol Med. 2017 Sep 15;49(9):e377. doi: 10.1038/emm.2017.135. Exp Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28912572 Free PMC article.
-
Global analysis of mRNA half-lives and de novo transcription in a dinoflagellate, Karenia brevis.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 11;8(6):e66347. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066347. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23776661 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted inactivation of β1 integrin induces β3 integrin switching, which drives breast cancer metastasis by TGF-β.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Nov;24(21):3449-59. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-10-0776. Epub 2013 Sep 4. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 24006485 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Häggroth L., Mattsson C., Felding P., Nilsson I. M. (1986) Plasminogen activator inhibitors in plasma and platelets from patients with recurrent venous thrombosis and pregnant women. Thromb. Res. 42, 585–594 - PubMed
-
- Loskutoff D. J., Sawdey M., Mimuro J. (1989) Type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. Prog. Hemost. Thromb. 9, 87–115 - PubMed
-
- Sprengers E. D., Kluft C. (1987) Plasminogen activator inhibitors. Blood 69, 381–387 - PubMed
-
- Dellas C., Loskutoff D. J. (2005) Historical analysis of PAI-1 from its discovery to its potential role in cell motility and disease. Thromb. Haemost. 93, 631–640 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

