Macrophage mesenchymal migration requires podosome stabilization by filamin A
- PMID: 22334688
- PMCID: PMC3339984
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.307124
Macrophage mesenchymal migration requires podosome stabilization by filamin A
Abstract
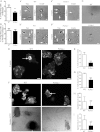
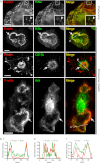
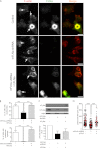
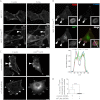
Filamin A (FLNa) is a cross-linker of actin filaments and serves as a scaffold protein mostly involved in the regulation of actin polymerization. It is distributed ubiquitously, and null mutations have strong consequences on embryonic development in humans, with organ defects which suggest deficiencies in cell migration. We have reported previously that macrophages, the archetypal migratory cells, use the protease- and podosome-dependent mesenchymal migration mode in dense three-dimensional environments, whereas they use the protease- and podosome-independent amoeboid mode in more porous matrices. Because FLNa has been shown to localize to podosomes, we hypothesized that the defects seen in patients carrying FLNa mutations could be related to the capacity of certain cell types to form podosomes. Using strategies based on FLNa knock-out, knockdown, and rescue, we show that FLNa (i) is involved in podosome stability and their organization as rosettes and three-dimensional podosomes, (ii) regulates the proteolysis of the matrix mediated by podosomes in macrophages, (iii) is required for podosome rosette formation triggered by Hck, and (iv) is necessary for mesenchymal migration but dispensable for amoeboid migration. These new functions assigned to FLNa, particularly its role in mesenchymal migration, could be directly related to the defects in cell migration described during the embryonic development in FLNa-defective patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanical strain in actin networks regulates FilGAP and integrin binding to filamin A.Nature. 2011 Sep 18;478(7368):260-3. doi: 10.1038/nature10430. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21926999 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage podosomes go 3D.Eur J Cell Biol. 2011 Feb-Mar;90(2-3):224-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2010.07.011. Eur J Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 20801545
-
RefilinB (FAM101B) targets filamin A to organize perinuclear actin networks and regulates nuclear shape.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jul 12;108(28):11464-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1104211108. Epub 2011 Jun 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21709252 Free PMC article.
-
Filamin A: phenotypic diversity.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2005 Jun;15(3):301-7. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2005.04.001. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2005. PMID: 15917206 Review.
-
The filamins: organizers of cell structure and function.Cell Adh Migr. 2011 Mar-Apr;5(2):160-9. doi: 10.4161/cam.5.2.14401. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Cell Adh Migr. 2011. PMID: 21169733 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hck contributes to bone homeostasis by controlling the recruitment of osteoclast precursors.FASEB J. 2013 Sep;27(9):3608-18. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-232736. Epub 2013 Jun 6. FASEB J. 2013. PMID: 23742809 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 uses dynamic podosomes for entry into macrophages.J Virol. 2021 Apr 26;95(10):e02480-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02480-20. Epub 2021 Feb 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33627394 Free PMC article.
-
Amotl2 interacts with LL5β, localizes to podosomes and regulates postsynaptic differentiation in muscle.J Cell Sci. 2013 May 15;126(Pt 10):2225-35. doi: 10.1242/jcs.121327. Epub 2013 Mar 22. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23525008 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Profiling of Retinoblastoma-Derived Exosomes Reveals Potential Biomarkers of Vitreous Seeding.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jun 12;12(6):1555. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061555. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32545553 Free PMC article.
-
Filamin A controls matrix metalloproteinase activity and regulates cell invasion in human fibrosarcoma cells.J Cell Sci. 2012 Aug 15;125(Pt 16):3858-69. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104018. Epub 2012 May 17. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22595522 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim H., McCulloch C. A. (2011) Filamin A mediates interactions between cytoskeletal proteins that control cell adhesion. FEBS Lett. 585, 18–22 - PubMed
-
- Zhou A. X., Hartwig J. H., Akyürek L. M. (2010) Filamins in cell signaling, transcription, and organ development. Trends Cell Biol. 20, 113–123 - PubMed
-
- Nakamura F., Osborn E., Janmey P. A., Stossel T. P. (2002) Comparison of filamin A-induced cross-linking and Arp2/3 complex-mediated branching on the mechanics of actin filaments. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 9148–9154 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

