Influence of charge ratio of liposome/DNA complexes on their size after extrusion and transfection efficiency
- PMID: 22334773
- PMCID: PMC3273975
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S27471
Influence of charge ratio of liposome/DNA complexes on their size after extrusion and transfection efficiency
Abstract
Background: Physicochemical characteristics of liposome/DNA complexes influence transfection efficiency and affect each other in a very intricate way. The result of this is discrepancies in conclusions drawn about the individual influence of each one.
Methods: Aiming to elucidate the influence of liposome/DNA charge ratio and size on transfection efficiency and on each other, we used liposome/DNA complexes with charge ratio (+/-) in the range of 1-50 and extruded through membranes of 400, 200, and 100 nm. Plasmid DNA encoding green fluorescent protein was used to measure transfection efficiency by flow cytometry. Sizes of liposome/DNA complexes were measured by dynamic light scattering.
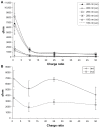
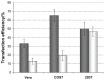
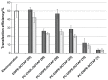
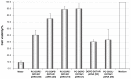
Results: Liposome size was reduced after extrusion but this was mainly driven by the charge ratio and not by the size of the membrane pores. Reduction of complex size at each charge ratio positively correlated with transfection efficiency. When the size of the complexes was approximately constant, increasing the charge ratio was found to promote transfection efficiency. Cationic lipid N-(1-(2,3-dioleoyloxy)propyl)N,N,N trimethylammonium chloride was used for modulation of positive charge and a cytotoxicity test showed that increasing its amount increases cytotoxicity.
Conclusion: It can be concluded that charge ratio dictates the size of the complex whereas overall size reduction and higher charge ratios promote transfection efficiency in vitro.
Keywords: liposome charge; liposome size; transfection efficiency.
Figures
References
-
- Wasungu L, Hoekstra D. Cationic lipids, lipoplexes and intracellular delivery of genes. J Control Release. 2006;116:255–264. - PubMed
-
- Karmali PP, Chaudhuri A. Cationic liposomes as non-viral carriers of gene medicines: resolved issues, open questiones, and future promises. Med Res Rev. 2007;27:696–722. - PubMed
-
- Gascon AR, Pedraz JL. Cationic lipids as gene transfer agents: a patent review. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2008;18:515–524.
-
- Niidome T, Huang L. Gene therapy progress and prospects: nonviral vectors. Gene Ther. 2002;9:1647–1652. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

