Localized AL amyloidosis: a suicidal neoplasm?
- PMID: 22335280
- PMCID: PMC3339556
- DOI: 10.3109/03009734.2012.654861
Localized AL amyloidosis: a suicidal neoplasm?
Abstract
Although AL amyloidosis usually is a systemic disease, strictly localized AL deposits are not exceptionally rare. Such case reports form a considerable body of published articles. Although both AL amyloidosis types are formed from an N-terminal segment of a monoclonal immunoglobulin light chain, a typical localized AL amyloid differs from the systemic counterpart by the morphological appearance of the amyloid, and presence of clonal plasma cells and of giant cells. In this article it is pointed out that localized AL amyloidosis ('amyloidoma') represents a true plasma cell neoplasm and not a pseudotumor. The pathogenesis of localized AL amyloidosis may differ from that of the systemic type, a suggestion underlined by the fact that localized AL amyloidosis of kappa type is as common as that of lambda origin, in contrast to the systemic form where lambda chains constitute the overwhelming majority of cases. It is suggested that oligomeric assemblies of the produced immunoglobulin light chain are toxic to plasma cells, which in this way commit suicide.
Figures

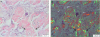

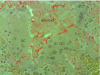

References
-
- Jarrett JT, Lansbury PT. Seeding "one-dimensional crystallization" of amyloid: a pathogenic mechanism in Alzheimer's disease and scrapie? Cell. 1993;73:1055–8. - PubMed
-
- Bhagwandeen BS, Taylor S. Primary localized amyloidosis of the bladder with a monoclonal plasma cell infiltrate. Pathology. 1988;20:67–9. - PubMed
-
- Monge M, Chauveau D, Cordonnier C, Noël LH, Presne C, Makdassi R, et al. Localized amyloidosis of the genitourinary tract: report of 5 new cases and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 2011;90:212–22. - PubMed
-
- Sipe JD, Benson MD, Buxbaum JN, Ikeda S, Merlini G, Saraiva MJ, et al. Amyloid fibril protein nomenclature: 2010 recommendations of the nomenclature committee of the International Society of Amyloidosis. Amyloid. 2010;17:101–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
