Interventions for covert bacteriuria in children
- PMID: 22336827
- PMCID: PMC11586096
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006943.pub2
Interventions for covert bacteriuria in children
Abstract
Background: Many studies investigating covert bacteriuria in children were conducted in the 1970s, but uncertainty remains about whether treatment is beneficial, because results are mixed in terms of treatment effectiveness. It is important to establish the effectiveness of antibiotics and other treatments to eliminate infection, reduce recurrence, and prevent long-term kidney damage. It is essential that treatment benefit to individual children outweigh any harm.
Objectives: This review aims to evaluate the benefits and harms of treating covert bacteriuria in children.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL in The Cochrane Library), MEDLINE (from 1966) and EMBASE (from 1988) without language restriction.Date of last search: 28 December 2011
Selection criteria: We included randomised and quasi-randomised controlled trials that investigated any intervention for covert bacteriuria in children aged up to 18 years with culture-proven urinary tract infection (UTI) and no known urinary symptoms at the time of diagnosis.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently assessed study quality and extracted data. Statistical analyses were performed using the random-effects model and the results were expressed as risk ratios (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) for dichotomous outcomes and mean difference (MD) for continuous outcomes.
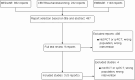
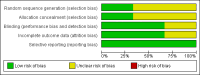
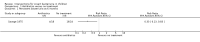
Main results: This review included three randomised controlled trials (RCTs) that involved 460 children (all girls). Overall, the studies were not methodologically strong. Gaps in reporting among the included studies made assessment of methodological quality challenging. One study reported that the number of children with bacteriuria was significantly reduced at follow-up six months after antibiotic treatment (RR 0.33; 95% CI 0.13 to 0.83). At follow-up two years after treatment, two studies reported that there was no evidence of a reduction in persistent bacteriuria (RR 0.32; 95% CI 0.03 to 3.44). At follow-up four to five years after initial treatment, all included studies reported that antibiotic treatment was effective in reducing the number of children with bacteriuria (RR 0.54; 95% CI 0.42 to 0.70). There were no differences in kidney growth between treated and untreated groups (MD 0.62; 95% CI -0.43 to 1.68).None of the included studies reported data on compliance or adverse effects.
Authors' conclusions: The included studies do not provide sufficient detail about the harms and benefits of treating covert bacteriuria to enable formation of reliable conclusions. It appears that antibiotic treatment for covert bacteriuria is unlikely to benefit children in the long term.
Conflict of interest statement
Anita Fitzgerald: Some of this work was undertaken when all authors were employed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women's and Children's Health, which received funding from NICE. The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and not necessarily those of NICE.
Rintaro Mori: none known
Monica Lakhanpaul: I was the Clinical Director at the National Collaborating Centre for Women's Health and led the development of the NICE Urinary Tract Infection Guideline. I am no longer the Clincial Director but remain on the NCC‐WCH board and I am a NICE Fellow and member of the NHS evidence advisory team.
Figures






Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
COBSG 1978 {published data only}
-
- Asscher AW, McLachlan MS, Jones RV, Meller S, Sussman M, Harrison S, et al. Screening for asymptomatic urinary‐tract infection in schoolgirls. A two‐centre feasibility study. Lancet 1973;2(7819):1‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Cardiff‐Oxford Bacteriuria Study Group. Sequelae of covert bacteriuria in schoolgirls. A four‐year follow‐up study. Lancet 1978;1(8070):889‐93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
NCBRG 1981 {published data only}
Savage 1975 {published data only}
-
- Savage DC, Howie G, Adler K, Wilson MI. Controlled trial of therapy in covert bacteriuria of childhood. Lancet 1975;1(7903):358‐61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Aggarwal 1991 {published data only}
Davison 1984 {published data only}
-
- Davison JM, Sprott MS, Selkon JB. The effect of covert bacteriuria in schoolgirls on renal function at 18 years and during pregnancy. Lancet 1984;2(8404):651‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lohr 1977 {published data only}
-
- Lohr JA, Nunley DH, Howards SS, Ford RF. Prevention of recurrent urinary tract infections in girls. Pediatrics 1977;59(4):562‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Verrier Jones 1982 {published data only}
-
- Verrier Jones K, Asscher AW, Verrier Jones ER, Mattholie K, Leach K, Thomson GM. Glomerular filtration rate in schoolgirls with covert bacteriuria. British Medical Journal 1982;285(6351):1307‐10. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Additional references
Bagga 2003
-
- Bagga A, Tripathi P, Jatana V, Hari P, Kapil A, Srivastava RN, et al. Bacteriuria and urinary tract infections in malnourished children. Pediatric Nephrology 2003;18(4):366‐70. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Brundtland 1973
-
- Brundtland GH, Hovig B. Screening for bacteriuria in school‐girls. An evaluation of a dip‐slide culture methods and the urinary glucose method. American Journal of Epidemiology 1973;97(4):246‐54. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Fallahzadeh 2006
-
- Fallahzadeh MH, Ghane F. Urinary tract infection in infants and children with diarrhoea. Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal 2006;12(5):690‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Fitzgerald 2007
Hansson 1989
-
- Hansson S, Jodal U, Norén L, Bjure J. Untreated bacteriuria in asymptomatic girls with renal scarring. Pediatrics 1989;84(6):964‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Iitaka 1990
-
- Iitaka K, Sakai T, Oyama K, Izawa T, Igarashi S. Screening for bacteriuria in Japanese school children. Acta Paediatrica Japonica 1990;32(6):690‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kemper 1992
-
- Kemper KJ, Avner ED. The case against screening urinalyses for asymptomatic bacteriuria in children. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1992;146(3):343‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kunin 1964
-
- Kunin C, Deutscher R, Paquin A. Urinary tract infection in school children; an epidemiologic, clinical and laboratory study. Medicine 1964;43:91‐130. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lefebvre 2011
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: searching for studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Lindberg 1978
-
- Lindberg U, Claesson I, Hanson LA, Jodal U. Asymptomatic bacteriuria in schoolgirls. VIII. Clinical course during a 3‐year follow‐up. Journal of Pediatrics 1978;92(2):194‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Meadow 1969
Newcastle Group 1975
NICE 2007
-
- National Collaborating Centre for Women’s and Children’s Health. Urinary tract infection in children. http://www.nice.org.uk/nicemedia/pdf/CG54fullguideline.pdf (accessed December 2011).
Savage 1973
Smaill 2007
-
- Smaill FM, Vazquez JC. Antibiotics for asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2007, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000490.pub2] - DOI
Stanley 2005
-
- Stanley R, Pagon Z, Bachur R. Hyperpyrexia among infants younger than 3 months. Pediatric Emergency Care 2005;21(5):291‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Villar 2009
Zainal 1994
-
- Zainal D, Baba A. Screening for bacteriuria in Malaysian school children. Singapore Medical Journal 1994;35(4):374‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

