Functional complexity and regulation through RNA dynamics
- PMID: 22337051
- PMCID: PMC3320162
- DOI: 10.1038/nature10885
Functional complexity and regulation through RNA dynamics
Abstract
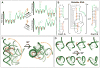
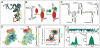
Changes to the conformation of coding and non-coding RNAs form the basis of elements of genetic regulation and provide an important source of complexity, which drives many of the fundamental processes of life. Although the structure of RNA is highly flexible, the underlying dynamics of RNA are robust and are limited to transitions between the few conformations that preserve favourable base-pairing and stacking interactions. The mechanisms by which cellular processes harness the intrinsic dynamic behaviour of RNA and use it within functionally productive pathways are complex. The versatile functions and ease by which it is integrated into a wide variety of genetic circuits and biochemical pathways suggests there is a general and fundamental role for RNA dynamics in cellular processes.
Figures


References
-
- Kendrew JC, et al. A three-dimensional model of the myoglobin molecule obtained by x-ray analysis. Nature. 1958;181:662–666. - PubMed
-
- Rould MA, Perona JJ, Soll D, Steitz TA. Structure of E. coli glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase complexed with tRNA(Gln) and ATP at 2.8 A resolution. Science. 1989;246:1135–1142. - PubMed
-
- Pley HW, Flaherty KM, McKay DB. Three-dimensional structure of a hammerhead ribozyme. Nature. 1994;372:68–74. - PubMed
-
- Scott WG, Finch JT, Klug A. The crystal structure of an all-RNA hammerhead ribozyme: a proposed mechanism for RNA catalytic cleavage. Cell. 1995;81:991–1002. - PubMed
-
- Wang S, Karbstein K, Peracchi A, Beigelman L, Herschlag D. Identification of the hammerhead ribozyme metal ion binding site responsible for rescue of the deleterious effect of a cleavage site phosphorothioate. Biochemistry. 1999;38:14363–14378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

