Systematic identification of the HSP90 candidate regulated proteome
- PMID: 22337586
- PMCID: PMC3433914
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M111.016675
Systematic identification of the HSP90 candidate regulated proteome
Abstract
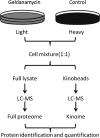
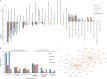
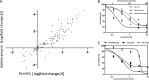
HSP90 is a central player in the folding and maturation of many proteins. More than two hundred HSP90 clients have been identified by classical biochemical techniques including important signaling proteins with high relevance to human cancer pathways. HSP90 inhibition has thus become an attractive therapeutic concept and multiple molecules are currently in clinical trials. It is therefore of fundamental biological and medical importance to identify, ideally, all HSP90 clients and HSP90 regulated proteins. To this end, we have taken a global and a chemical proteomic approach in geldanamycin treated cancer cell lines using stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture and quantitative mass spectrometry. We identified >6200 proteins in four different human cell lines and ~1600 proteins showed significant regulation upon drug treatment. Gene ontology and pathway/network analysis revealed common and cell-type specific regulatory effects with strong connections to unfolded protein binding and protein kinase activity. Of the 288 identified protein kinases, 98 were geldanamycin treatment including >50 kinases not formerly known to be regulated by HSP90. Protein turn-over measurements using pulsed stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture showed that protein down-regulation by HSP90 inhibition correlates with protein half-life in many cases. Protein kinases show significantly shorter half lives than other proteins highlighting both challenges and opportunities for HSP90 inhibition in cancer therapy. The proteomic responses of the HSP90 drugs geldanamycin and PU-H71 were highly similar suggesting that both drugs work by similar molecular mechanisms. Using HSP90 immunoprecipitation, we validated several kinases (AXL, DDR1, TRIO) and other signaling proteins (BIRC6, ISG15, FLII), as novel clients of HSP90. Taken together, our study broadly defines the cellular proteome response to HSP90 inhibition and provides a rich resource for further investigation relevant for the treatment of cancer.
Figures



References
-
- Taipale M., Jarosz D. F., Lindquist S. (2010) HSP90 at the hub of protein homeostasis: emerging mechanistic insights. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 11, 515–528 - PubMed
-
- Picard D. HSP90 interactors. http://www.picard.ch/downloads/Hsp90interactors.pdf
-
- Zhao R., Houry W. A. (2007) Molecular interaction network of the Hsp90 chaperone system. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 594, 27–36 - PubMed
-
- Whitesell L., Lindquist S. L. (2005) HSP90 and the chaperoning of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 5, 761–772 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

