Developmental changes in the inferior frontal cortex for selecting semantic representations
- PMID: 22337757
- PMCID: PMC3278275
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dcn.2011.01.005
Developmental changes in the inferior frontal cortex for selecting semantic representations
Abstract
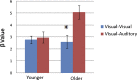
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) was used to examine the neural correlates of semantic judgments to Chinese words in a group of 10-15 year old Chinese children. Two semantic tasks were used: visual-visual versus visual-auditory presentation. The first word was visually presented (i.e. character) and the second word was either visually or auditorily presented, and the participant had to determine if these two words were related in meaning. Different from English, Chinese has many homophones in which each spoken word corresponds to many characters. The visual-auditory task, therefore, required greater engagement of cognitive control for the participants to select a semantically appropriate answer for the second homophonic word. Weaker association pairs produced greater activation in the mid-ventral region of left inferior frontal gyrus (BA 45) for both tasks. However, this effect was stronger for the visual-auditory task than for the visual-visual task and this difference was stronger for older compared to younger children. The findings suggest greater involvement of semantic selection mechanisms in the cross-modal task requiring the access of the appropriate meaning of homophonic spoken words, especially for older children.
Keywords: Age; Association strength; Auditory; Semantic; Visual; fMRI.
Figures


References
-
- Adleman N.E., Blasey C.M., White C.D., Warsofsky I.S., Glover G.H., Reiss A.L. A developmental functional fMRI study of the Stroop color-word task. NeuroImage. 2002;16:61–75. - PubMed
-
- Amedi A., von Kriegstein K., van Atteveldt N.M., Beauchamp M.S., Naumer M.J. Functional imaging of human crossmodal identification and object recognition. Experimental Brain Research. 2005;166:559–571. - PubMed
-
- Badre D., Poldrack R.A., Pare-Blagoev E.J., Insler R.Z., Wagner A.D. Dissociable controlled retrieval and generalized selection mechanisms in ventrolateral prefrontal cortex. Neuron. 2005;47:907–918. - PubMed
-
- Badre D., Wagner A.D. Left ventrolateral prefrontal cortex and the cognitive control of memory. Neuropsychologia. 2007;45:2883–2901. - PubMed
-
- Barnea-Goraly N., Menon V., Eckert M., Tamm L., Bammer R., Karchemskiy A., Dant C.C., Reiss A.L. White matter development during childhood and adolescence: a cross-sectional diffusion tensor imaging study. Cerebral Cortex. 2005;15(12):1848–1854. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

