Sequence typing confirms that a predominant Listeria monocytogenes clone caused human listeriosis cases and outbreaks in Canada from 1988 to 2010
- PMID: 22337989
- PMCID: PMC3347097
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.06185-11
Sequence typing confirms that a predominant Listeria monocytogenes clone caused human listeriosis cases and outbreaks in Canada from 1988 to 2010
Abstract
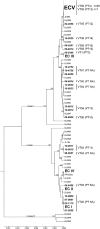
Human listeriosis outbreaks in Canada have been predominantly caused by serotype 1/2a isolates with highly similar pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) patterns. Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) and multi-virulence-locus sequence typing (MVLST) each identified a diverse population of Listeria monocytogenes isolates, and within that, both methods had congruent subtypes that substantiated a predominant clone (clonal complex 8; virulence type 59; proposed epidemic clone 5 [ECV]) that has been causing human illness across Canada for more than 2 decades.
Figures
References
-
- Chen Y, Knabel S. 2008. Strain typing. In Liu D. (ed), Handbook of Listeria monocytogenes. CRC Press, New York, NY
-
- Cheng Y, Siletzky RM, Kathariou S. 2008. Genomic divisions/lineages, epidemic clones, and population structure. In Liu D. (ed), Handbook of Listeria monocytogenes. CRC Press, New York, NY
-
- Clark CG, et al. 2010. Surveillance for Listeria monocytogenes and listeriosis, 1995-2004. Epidemiol. Infect. 138:559–572 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

