Dark-adapted response threshold of OFF ganglion cells is not set by OFF bipolar cells in the mouse retina
- PMID: 22338022
- PMCID: PMC3362285
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.01202.2011
Dark-adapted response threshold of OFF ganglion cells is not set by OFF bipolar cells in the mouse retina
Abstract
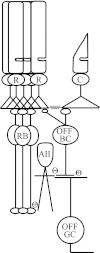
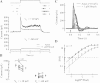
The nervous system frequently integrates parallel streams of information to encode a broad range of stimulus strengths. In mammalian retina it is generally believed that signals generated by rod and cone photoreceptors converge onto cone bipolar cells prior to reaching the retinal output, the ganglion cells. Near absolute visual threshold a specialized mammalian retinal circuit, the rod bipolar pathway, pools signals from many rods and converges on depolarizing (AII) amacrine cells. However, whether subsequent signal flow to OFF ganglion cells requires OFF cone bipolar cells near visual threshold remains unclear. Glycinergic synapses between AII amacrine cells and OFF cone bipolar cells are believed to relay subsequently rod-driven signals to OFF ganglion cells. However, AII amacrine cells also make glycinergic synapses directly with OFF ganglion cells. To determine the route for signal flow near visual threshold, we measured the effect of the glycine receptor antagonist strychnine on response threshold in fully dark-adapted retinal cells. As shown previously, we found that response threshold for OFF ganglion cells was elevated by strychnine. Surprisingly, strychnine did not elevate response threshold in any subclass of OFF cone bipolar cell. Instead, in every OFF cone bipolar subclass strychnine suppressed tonic glycinergic inhibition without altering response threshold. Consistent with this lack of influence of strychnine, we found that the dominant input to OFF cone bipolar cells in darkness was excitatory and the response threshold of the excitatory input varied by subclass. Thus, in the dark-adapted mouse retina, the high absolute sensitivity of OFF ganglion cells cannot be explained by signal transmission through OFF cone bipolar cells.
Figures


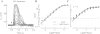




References
-
- Bloomfield SA, Dacheux RF. Rod vision: pathways and processing in the mammalian retina. Prog Retin Eye Res 20: 351–384, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Chang B, Dacey MS, Hawes NL, Hitchcock PF, Milam AH, Atmaca-Sonmez P, Nusinowitz S, Heckenlively JR. Cone photoreceptor function loss-3, a novel mouse model of achromatopsia due to a mutation in Gnat2. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47: 5017–5021, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

