Bed rest impairs skeletal muscle amino acid transporter expression, mTORC1 signaling, and protein synthesis in response to essential amino acids in older adults
- PMID: 22338078
- PMCID: PMC3361979
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00603.2011
Bed rest impairs skeletal muscle amino acid transporter expression, mTORC1 signaling, and protein synthesis in response to essential amino acids in older adults
Abstract
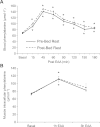
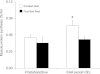
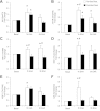
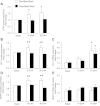
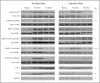
Skeletal muscle atrophy during bed rest is attributed, at least in part, to slower basal muscle protein synthesis (MPS). Essential amino acids (EAA) stimulate mammalian target of rapamycin (mTORC1) signaling, amino acid transporter expression, and MPS and are necessary for muscle mass maintenance, but there are no data on the effect of inactivity on this anabolic mechanism. We hypothesized that bed rest decreases muscle mass in older adults by blunting the EAA stimulation of MPS through reduced mTORC1 signaling and amino acid transporter expression in older adults. Six healthy older adults (67 ± 2 yr) participated in a 7-day bed rest study. We used stable isotope tracers, Western blotting, and real-time qPCR to determine the effect of bed rest on MPS, muscle mTORC1 signaling, and amino acid transporter expression and content in the postabsorptive state and after acute EAA ingestion. Bed rest decreased leg lean mass by ∼4% (P < 0.05) and increased postabsorptive mTOR protein (P < 0.05) levels while postabsorptive MPS was unchanged (P > 0.05). Before bed rest acute EAA ingestion increased MPS, mTOR (Ser(2448)), S6 kinase 1 (Thr(389), Thr(421)/Ser(424)), and ribosomal protein S6 (Ser(240/244)) phosphorylation, activating transcription factor 4, L-type amino acid transporter 1 and sodium-coupled amino acid transporter 2 protein content (P < 0.05). However, bed rest blunted the EAA-induced increase in MPS, mTORC1 signaling, and amino acid transporter protein content. We conclude that bed rest in older adults significantly attenuated the EAA-induced increase in MPS with a mechanism involving reduced mTORC1 signaling and amino acid transporter protein content. Together, our data suggest that a blunted EAA stimulation of MPS may contribute to muscle loss with inactivity in older persons.
Figures

References
-
- Adams CM. Role of the transcription factor ATF4 in the anabolic actions of insulin and the anti-anabolic actions of glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem 282: 16744–16753, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Baird FE, Bett KJ, MacLean C, Tee AR, Hundal HS, Taylor PM. Tertiary active transport of amino acids reconstituted by coexpression of System A and L transporters in Xenopus oocytes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 297: E822–E829, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Berg HE, Tedner B, Tesch PA. Changes in lower limb muscle cross-sectional area and tissue fluid volume after transition from standing to supine. Acta Physiol Scand 148: 379–385, 1993 - PubMed
-
- Burd NA, West DW, Moore DR, Atherton PJ, Staples AW, Prior T, Tang JE, Rennie MJ, Baker SK, Phillips SM. Enhanced amino acid sensitivity of myofibrillar protein synthesis persists for up to 24 h after resistance exercise in young men. J Nutr 141: 568–573, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Calder AG, Anderson SE, Grant I, McNurlan MA, Garlick PJ. The determination of low d5-phenylalanine enrichment (0.002–009 atom percent excess), after conversion to phenylethylamine, in relation to protein turnover studies by gas chromatography/electron ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass spectrom 6: 421–424, 1992 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

