Target-mediated pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic model of exendin-4 in rats, monkeys, and humans
- PMID: 22338110
- PMCID: PMC3336795
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.111.042291
Target-mediated pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic model of exendin-4 in rats, monkeys, and humans
Abstract
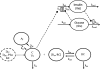
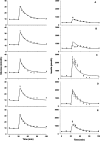
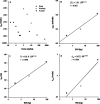
A mechanism-based pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) model was developed for exendin-4 to account for receptor-mediated endocytosis via glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP-1R) as the primary mechanism for its nonlinear disposition. Time profiles of exendin-4 concentrations after intravenous, subcutaneous, and continuous intravenous infusion doses in rats, intravenous and subcutaneous doses in monkeys, and intravenous infusion and subcutaneous doses in humans were examined. Mean data for glucose and insulin after glucose challenges during exendin-4 treatment in healthy rats were analyzed. The PK model components included receptor binding, subsequent internalization and degradation, nonspecific tissue distribution, and linear first-order elimination from plasma. The absorption rate constant (k(a)) decreased with increasing doses in all three species. The clearance from the central compartment (CL(c)) (rats, 3.62 ml/min; monkeys, 2.39 ml · min(-1) · kg(-1); humans, 1.48 ml · min(-1) · kg(-1)) was similar to reported renal clearances. Selected PK parameters (CL(c), V(c), and k(off)) correlated allometrically with body weight. The equilibrium dissociation constant (K(D)) was within the reported range in rats (0.74 nM), whereas the value in monkeys (0.12 pM) was much lower than that in humans (1.38 nM). The effects of exendin-4 on the glucose-insulin system were described by a feedback model with a biphasic effect equation driven by free exendin-4 concentrations. Our generalized nonlinear PK/PD model for exendin-4 taking into account of drug binding to GLP-1R well described PK profiles after various routes of administration over a large range of doses in three species along with PD responses in healthy rats. The present model closely reflects underlying mechanisms of disposition and dynamics of exendin-4.
Figures
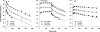




Similar articles
-
Biological activity of AC3174, a peptide analog of exendin-4.Regul Pept. 2007 Jun 7;141(1-3):113-9. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2006.12.021. Epub 2007 Jan 11. Regul Pept. 2007. PMID: 17292977
-
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling of exendin-4 in type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Mar;336(3):881-90. doi: 10.1124/jpet.110.175752. Epub 2010 Dec 14. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011. PMID: 21156817 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term metabolic benefits of exenatide in mice are mediated solely via the known glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2014 Apr 1;306(7):R490-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00495.2013. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24477544
-
Pharmacokinetic drug evaluation of exenatide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2018 Feb;14(2):207-217. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2018.1420160. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29260924 Review.
-
Pharmacology of exenatide (synthetic exendin-4): a potential therapeutic for improved glycemic control of type 2 diabetes.Regul Pept. 2004 Feb 15;117(2):77-88. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2003.10.028. Regul Pept. 2004. PMID: 14700743 Review.
Cited by
-
Population pharmacokinetics of exenatide.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2017 Mar;83(3):517-526. doi: 10.1111/bcp.13135. Epub 2016 Nov 16. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27650681 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of serum FABP4 level by sitagliptin, a DPP-4 inhibitor, in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Lipid Res. 2015 Dec;56(12):2372-80. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M059469. Epub 2015 Oct 14. J Lipid Res. 2015. PMID: 26467280 Free PMC article.
-
Model-Based Evaluation of Exenatide Effects on the QT Interval in Healthy Subjects Following Continuous IV Infusion.J Clin Pharmacol. 2017 Aug;57(8):956-965. doi: 10.1002/jcph.882. Epub 2017 May 22. J Clin Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28543393 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Disconnect between signalling potency and in vivo efficacy of pharmacokinetically optimised biased glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists.Mol Metab. 2020 Jul;37:100991. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.100991. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Mol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32278079 Free PMC article.
-
Implementation of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic strategies in early research phases of drug discovery and development at Novartis Institute of Biomedical Research.Front Pharmacol. 2014 Jul 28;5:174. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2014.00174. eCollection 2014. Front Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25120485 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adair GS. (1923) On the Donnan Equilibrium and the Equation of Gibbs. Science 58:13. - PubMed
-
- Ai G, Chen Z, Shan C, Che J, Hou Y, Cheng Y. (2008) Single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of exendin-4 in rhesus monkeys. Int J Pharm 353:56–64 - PubMed
-
- Altaian PL, Dittmer DS. (1974) Renal function test: vertebrates, in Biology Data Book, 2nd ed, vol 3, pp 562–572, Federation of the American Societies for Experimental Biology, Bethesda
-
- Copley K, McCowen K, Hiles R, Nielsen LL, Young A, Parkes DG. (2006) Investigation of exenatide elimination and its in vivo and in vitro degradation. Curr Drug Metab 7:367–374 - PubMed
-
- Cvetković RS, Plosker GL. (2007) Exenatide: a review of its use in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (as an adjunct to metformin and/or a sulfonylurea). Drugs 67:935–954 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

