Convection enhanced delivery of macromolecules for brain tumors
- PMID: 22339074
- PMCID: PMC7521418
- DOI: 10.2174/157016312803305951
Convection enhanced delivery of macromolecules for brain tumors
Abstract
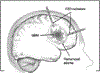
The blood brain barrier (BBB) poses a significant challenge for drug delivery of macromolecules into the brain. Convection-enhanced delivery (CED) circumvents the BBB through direct intracerebral infusion using a hydrostatic pressure gradient to transfer therapeutic compounds. The efficacy of CED is dependent on the distribution of the therapeutic agent to the targeted region. Here we present a review of convection enhanced delivery of macromolecules, emphasizing the role of tracers in enabling effective delivery anddiscuss current challenges in the field.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
None declared.
References
-
- Kanu OO, Mehta A, Di C, et al. Glioblastoma multiforme: a review of therapeutic targets. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2009; 13(6): 701–18. - PubMed
-
- Reardon DA, Rich JN, Friedman HS, et al. Recent advances in the treatment of malignant astrocytoma. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24(8): 1253–65. - PubMed
-
- Muldoon LL, Soussain C, Jahnke K, et al. Chemotherapy delivery issues in central nervous system malignancy: a reality check. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25(16): 2295–305. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical