Pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of Bencycloquidium bromide, a novel selective muscarinic M1/M3 receptor antagonist, after single and multiple intranasal doses in healthy chinese subjects: an open-label, single-center, first-in-human study
- PMID: 22339483
- PMCID: PMC3585954
- DOI: 10.2165/11599330-000000000-00000
Pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of Bencycloquidium bromide, a novel selective muscarinic M1/M3 receptor antagonist, after single and multiple intranasal doses in healthy chinese subjects: an open-label, single-center, first-in-human study
Abstract
Background: Bencycloquidium bromide (BCQB) is a novel, potent and selective muscarinic M1/M3 receptor antagonist under development for the treatment of rhinorrhea in rhinitis. The pharmacokinetics and safety of BCQB in animals have been established in preclinical studies. However, no clinical pharmacokinetic data are available for BCQB in humans.
Objective: The aim of this first-in-human study was to evaluate the pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of BCQB following single and multiple intranasal doses in healthy Chinese subjects.
Methods: The clinical trial was comprised of the following four studies: (i) an open-label, single-dose escalation study to evaluate the safety and tolerability in healthy subjects after intranasal doses of BCQB ranging from 45 to 450 μg (total of six doses); (ii) an open-label, multiple-dose escalation study to assess the safety and tolerability in healthy subjects after intranasal administration with 120 and 150 μg doses of BCQB (360 and 450 μg/day) administered three times daily for 15 days; (iii) a randomized, open-label and parallel-group design to evaluate the single-dose pharmacokinetics of BCQB after intranasal dosing (45, 90, and 180 μg); and (iv) ten subjects received 120 μg of BCQB by intranasal administration, three times daily for 5 days with a final single dose on day 7 to assess its multiple-dose pharmacokinetics. Safety and tolerability of BCQB were evaluated by monitoring adverse events (AEs), ECG recordings, vital signs and clinical laboratory parameters. The pharmacokinetic parameters for BCQB were calculated by software using non-compartmental methods.
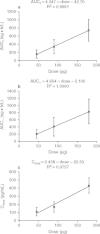
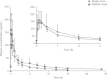
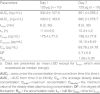
Results: All AEs were mild, of limited duration and no more frequent at higher doses. There was no serious adverse event, death or withdrawal. No clinically significant change was noted in clinical laboratory parameters, cardiac parameters or vital signs. Following single intranasal dosing, BCQB was rapidly absorbed with a median time to maximum concentration (t(max)) of 8 minutes for 45, 90, and 180 μg dose groups; the plasma concentration of BCQB decreased in a biphasic manner with the mean half-life (t(½)) of 8.5 hours; the maximum concentration (C(max)) and area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) of BCQB increased linearly across the examined dose range of 45-180 μg. During the multiple dosing, the steady state was achieved within 3 days of 120 μg three times daily dosing of BCQB. A slightly greater AUC was observed after 5 days of multiple dosing, with the mean accumulation ratio of 1.26; however, the half-life was unchanged.
Conclusion: BCQB was safe and well tolerated in healthy Chinese subjects when administered intranasally with single and multiple doses across the doses studied. The mean C(max) and AUC increased proportionally to the studied doses, and the steady state was achieved within 3 days after three times daily dosing. A slight accumulation of BCQB following multiple dosing was observed. The pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability profiles of BCQB pose it as a good candidate for further development in the treatment of rhinorrhea in rhinitis.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Safety, Tolerability and Pharmacokinetics of Bencycloquidium Bromide, a Novel Inhaled Anticholinergic Bronchodilator, in Healthy Subjects: Results from Phase I Studies.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021 Feb 1;157:105646. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105646. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 33220462 Clinical Trial.
-
Study of pharmacokinetic interaction of paroxetine and roxithromycin on bencycloquidium bromide in healthy subjects.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2015 Mar 10;69:37-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2014.12.019. Epub 2015 Jan 2. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2015. PMID: 25559065 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetic Study of 101BHG-D01 Nasal Spray, a Novel Long-Acting and Selective Cholinergic M Receptor Antagonist, in Healthy Chinese Volunteers: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Single-Dose Escalation, First-In-Human Study.Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2022 Jul;47(4):509-521. doi: 10.1007/s13318-022-00769-6. Epub 2022 Apr 16. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2022. PMID: 35429285 Clinical Trial.
-
Reviewing the role of healthy volunteer studies in drug development.J Transl Med. 2018 Dec 4;16(1):336. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1710-5. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30509294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple Dose Pharmacokinetic Study of Meropenem in Young Infants (<91 days) with Suspected or Complicated Intra-abdominal Infections [Internet].Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (US); 2011 Jul 15. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (US); 2011 Jul 15. PMID: 36630542 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Long-Acting Muscarinic Antagonists Under Investigational to Treat Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.J Exp Pharmacol. 2020 Dec 8;12:559-574. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S259330. eCollection 2020. J Exp Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33324119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[A multi-center observation of the therapeutic efficacy of Bencycloquidium bromide in the treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis with predominant symptoms of rhinorrhea].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Jul;37(7):550-555. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.07.008. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37549947 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Effects of ABCB1, UGT1A1, and UGT1A9 Genetic Polymorphisms on the Pharmacokinetics of Sitafloxacin Granules in Healthy Subjects.Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2021 Jan;10(1):57-67. doi: 10.1002/cpdd.848. Epub 2020 Jul 20. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2021. PMID: 32687695 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Bencycloquidium bromide inhibits nasal hypersecretion in a rat model of allergic rhinitis.Inflamm Res. 2015 Apr;64(3-4):213-23. doi: 10.1007/s00011-015-0800-6. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Inflamm Res. 2015. PMID: 25690567
-
Structure, function and drug discovery of GPCR signaling.Mol Biomed. 2023 Dec 4;4(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s43556-023-00156-w. Mol Biomed. 2023. PMID: 38047990 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

