Attenuation of influenza virus infectivity with herbal-marine compound (HESA-A): an in vitro study in MDCK cells
- PMID: 22340010
- PMCID: PMC3296628
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-44
Attenuation of influenza virus infectivity with herbal-marine compound (HESA-A): an in vitro study in MDCK cells
Abstract
Background: The influenza virus is still one of the most important respiratory risks affecting humans which require effective treatments. In this case, traditional medications are of interest. HESA-A is an active natural biological compound from herbal-marine origin. Previous studies have reported that the therapeutic properties of HESA-A are able to treat psoriasis vulgaris and cancers. However, no antiviral properties have been reported.
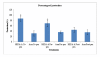
Methods: This study was designed to investigate the potential antiviral properties of HESA-A and its effects in modulating TNF-α and IL-6 cytokine levels. HESA-A was prepared in normal saline as a stock solution (0.8 mg/ml, pH = 7.4). Percentages of cell survival when exposed to different concentrations of HESA-A at different time intervals was determined by MTT assay. To study the potential antiviral activity of HESA-A, Madin-Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) cells were treated with the effective concentration (EC50) of HESA-A (0.025 mg/ml) and 100 TCID50/0.1 ml of virus sample under different types of exposure.
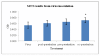
Results: Based on the MTT method and hemagglutination assay (HA), HESA-A is capable of improving cell viability to 31% and decreasing HA titre to almost 99% in co-penetration exposures. In addition, based on quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), it was found that HESA-A causes decrements in TNF-α and IL-6 cytokine expressions, which was significant for TNF-α (p ≤ 0.05) but not for IL-6.
Conclusion: In conclusion, HESA-A was effective against influenza infection through suppressing cytokine expression.
Figures
References
-
- Moallem S, Ahmadi A, Moshafi M, Taghavi M. Evaluation of fetal toxicity of HESA-A, a natural anticancer agent, in mice. J Kerman Univ Med Sci. 2007;14:124–133.
-
- Ahmadi A, Barikbin B, Naseri M, Mohagheghi M. The effect of HESA-A on psoriasis vulgaris. J Drugs Dermatol. 2008;7:559–561. - PubMed
-
- Ahmadi A, Mohagheghi M, Fazeli M, Nahavandian B, Bashardoost N, Musavi-Jarahi A, Gharipoor M. HESA-A, a new treatment for breast cancer and choroidal metastasis. Med Sci Monit. 2005;11:300–303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

